The Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Branched-Chain α-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase Kinase in Metabolic Disorders
- PMID: 35923208
- PMCID: PMC9339795
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.932670
The Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Branched-Chain α-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase Kinase in Metabolic Disorders
Abstract
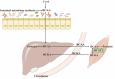
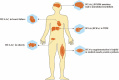
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), composed of leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are important essential amino acids in human physiology. Decades of studies have revealed their roles in protein synthesis, regulating neurotransmitter synthesis, and the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR). BCAAs are found to be related to many metabolic disorders, such as insulin resistance, obesity, and heart failure. Also, many diseases are related to the alteration of the BCAA catabolism enzyme branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase kinase (BCKDK), including maple syrup urine disease, human autism with epilepsy, and so on. In this review, diseases and the corresponding therapies are discussed after the introduction of the catabolism and detection methods of BCAAs and BCKDK. Also, the interaction between microbiota and BCAAs is highlighted.
Keywords: MALDI-MSI; branched-chain amino acids; branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase kinase; metabolic disorders; microbiota.
Copyright © 2022 Du, Liu, Yang, Zhao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diabetes and branched-chain amino acids: What is the link?J Diabetes. 2018 May;10(5):350-352. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12645. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29369529
-
The Critical Role of the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) Catabolism-Regulating Enzymes, Branched-Chain Aminotransferase (BCAT) and Branched-Chain α-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase (BCKD), in Human Pathophysiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 5;23(7):4022. doi: 10.3390/ijms23074022. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Brain Metabolism.Neurochem Res. 2017 Jun;42(6):1697-1709. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2261-5. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28417264 Review.
-
Pathophysiology of maple syrup urine disease: Focus on the neurotoxic role of the accumulated branched-chain amino acids and branched-chain α-keto acids.Neurochem Int. 2022 Jul;157:105360. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105360. Epub 2022 May 13. Neurochem Int. 2022. PMID: 35577033 Review.
-
Primary Roles of Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) and Their Metabolism in Physiology and Metabolic Disorders.Molecules. 2024 Dec 27;30(1):56. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010056. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39795113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota: The key to the treatment of metabolic syndrome in traditional Chinese medicine - a case study of diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 23;13:1072376. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1072376. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36618372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Microbiota-Associated Metabolites in Heart Failure.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 21;11(8):2313. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082313. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FGF21-dependent alleviation of cholestasis-induced liver fibrosis by sodium butyrate.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 8;15:1422770. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1422770. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39040469 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Homeostasis of Amino Acids and Diabetic Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 30;15(1):184. doi: 10.3390/nu15010184. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36615841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroactive Amino Acid Profile in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Results from a Clinical Sample.Children (Basel). 2023 Feb 20;10(2):412. doi: 10.3390/children10020412. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36832540 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

