SIRT3 inhibitor 3-TYP exacerbates thioacetamide-induced hepatic injury in mice
- PMID: 35923224
- PMCID: PMC9340259
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.915193
SIRT3 inhibitor 3-TYP exacerbates thioacetamide-induced hepatic injury in mice
Abstract
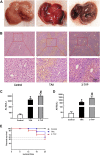
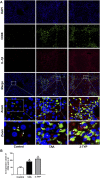
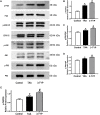
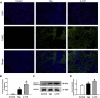
The purpose of the study was to explore the effects of SIRT3 inhibitor 3-TYP on acute liver failure (ALF) in mice and its underlying mechanism. The mice were treated with thioacetamide (TAA, 300 mg/kg) for inducing ALF model. 3-TYP (50 mg/kg) was administered 2 h prior to TAA. The liver histological changes were measured by HE staining. Blood samples were collected for analysis of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). MDA and GSH were used to evaluate the oxidative stress of liver. The expression levels of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β) were measured by ELISA and Western blotting. The cell type expression of IL-1β in liver tissue was detected by immunofluorescent staining. The expression of SIRT3, MnSOD, ALDH2, MAPK, NF-κB, Nrf2/HO-1, p-elF2α/CHOP, and cleaved caspase 3 was determined by Western blotting. TUNEL staining was performed to detect the apoptosis cells of liver tissues. 3-TYP exacerbated the liver injury of ALF mice. 3-TYP increased the inflammatory responses and activation of MAPK and NF-κB pathways. In addition, 3-TYP administration enhanced the damage of oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and promoted hepatocyte apoptosis in ALF mice. 3-TYP exacerbates thioacetamide-induced hepatic injury in mice. Activation of SIRT3 could be a promising target for the treatment of ALF.
Keywords: 3-TYP; SIRT3; acute liver failure; inflammation; thioacetamide.
Copyright © 2022 Shi, Jiao, Wang, Chen, Wang and Gong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective role of AGK2 on thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure in mice.Life Sci. 2019 Aug 1;230:68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.061. Epub 2019 May 23. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31129140
-
[Protective effect of water extracts of Orychophragmus violaceus seeds on TAA-induced acute liver injury in mice].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Mar;45(6):1399-1405. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20191112.405. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32281354 Chinese.
-
[Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in D-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver failure].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2014 May;22(5):364-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2014.05.009. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25180872 Chinese.
-
Pterostilbene Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide/D-Galactosamine-Induced Acute Liver Failure by Upregulating the Nrf2 Pathway and Inhibiting NF-κB, MAPK, and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.J Med Food. 2020 Sep;23(9):952-960. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2019.4647. Epub 2020 Jul 17. J Med Food. 2020. PMID: 32701014
-
Drug-induced-acute liver failure: A critical appraisal of the thioacetamide model for the study of hepatic encephalopathy.Toxicol Rep. 2021 Apr 30;8:962-970. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.04.011. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34026559 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sirtuin3 confers protection against acute pulmonary embolism through anti-inflammation, and anti-oxidative stress, and anti-apoptosis properties: participation of the AMP-activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway.Exp Anim. 2023 Aug 7;72(3):346-355. doi: 10.1538/expanim.22-0175. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Exp Anim. 2023. PMID: 36858596 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Linggui Zhugan Decoction protects against ventricular remodeling through ameliorating mitochondrial damage in post-myocardial infarction rats.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jan 10;9:1038523. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1038523. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36704451 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise enhancement by RGS14 disruption is mediated by brown adipose tissue.Aging Cell. 2023 Apr;22(4):e13791. doi: 10.1111/acel.13791. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Aging Cell. 2023. PMID: 36905127 Free PMC article.
-
Honokiol relieves hippocampal neuronal damage in Alzheimer's disease by activating the SIRT3-mediated mitochondrial autophagy.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Aug;30(8):e14878. doi: 10.1111/cns.14878. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39097923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beutler E., Duron O., Kelly B. M. (1963). Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 61, 882–888. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

