Deltamethrin Contact Exposure Mediated Toxicity and Histopathological Aberrations in Tissue Systems of Public Health Importance Cockroach Species Periplaneta americana and Blattella germanica
- PMID: 35923234
- PMCID: PMC9340665
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.926267
Deltamethrin Contact Exposure Mediated Toxicity and Histopathological Aberrations in Tissue Systems of Public Health Importance Cockroach Species Periplaneta americana and Blattella germanica
Abstract
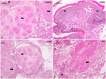
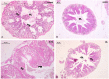
Cockroach species Periplaneta americana and Blattella germanica potentially survive in locations close to human activity. Besides spoiling food material, cockroaches also transfer pathogens of different diseases among human beings. Since the insecticides have been used extensively to control cockroaches, information on their insecticide susceptibility and toxicity at the cellular level may be crucial. In the study, deltamethrin toxicity as well as the deltamethrin-mediated cytomorphological changes in the brain, ovary and midgut of the two important cockroach species have been assessed. Different concentrations [0.00025% (0.0025 mg/ml), 0.0025% (0.025 mg/ml), 0.025% (0.25 mg/ml), 0.25% (2.5 mg/ml), 0.5% (5 mg/ml), 1% (10 mg/ml)] of deltamethrin in acetone were used to expose test species in WHO bottle assay. Knockdown was recorded after 5 min interval while delayed mortality was observed after 24 h. Brain, ovary and gut were dissected post 1 h exposure and 24 h holding (for 0.25, 0.5 and 1% concentration), and tissues were processed for microscopic analysis. Deltamethrin exposed cockroaches and dissected tissues were used to estimate deltamethrin using HPLC. At 0.00025% (lowest concentration), the percentage knock-down observed was 66.7% for P. americana and 80% B. germanica respectively (R 2 = 0.78; p = 0.0001) in 1 h. KDT50 value was found to be 8.7 min (95% CI: 7.3-10.2), while KDT99 was 20.7 min (95% CI: 16.0-35.7) in P. americana at 1% concentration. Whereas, the KDT50 and KDT99 values for B. germanica were 7.4 min (95% CI: 5.4-9.1) and 27.4 min (95% CI: 18.2-80.0) at a similar concentration. LD50 and LD95 values (for 60 min standard exposure) were 0.0006% (95% CI: 0.00-0.001) and 0.034% (95% CI: 0.013-0.49) respectively for P. americana, while these values were 0.0005 (95% CI: 0.00-0.001) and 0.04 (95% CI: 0.01-0.23) for B. germanica. Exposure to 1% deltamethrin induced a considerable toxic effect in the epithelial cells in the midgut. HPLC estimated 0.21 ± 0.05 mg (95% CI: 0.18-0.25; CoV 23.9%) deltamethrin in P. americana post 1% exposure. Even short term exposure to a low concentration of synthetic pyrethroid deltamethrin displayed immediate knockdown and delayed mortality in both the test species. Considerable histological damage was observed in both the insects at 1% exposure. In India, resistance to deltamethrin may have been reported among different insects due to its extensive use. However, the formulations such as insecticide paints, attractant baits etc. developed using deltamethrin as an active ingredient could be useful in cockroach control operations.
Keywords: Blattella germanica; Periplaneta americana; deltamethrin; knock-down; mortality; toxicity.
Copyright © 2022 Dhiman, Yadav, Acharya, Nagar and Rao Ghorpade.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel gene superfamilies of the cockroaches Blattella germanica and Periplaneta americana.Pest Manag Sci. 2021 Aug;77(8):3787-3799. doi: 10.1002/ps.6245. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Pest Manag Sci. 2021. PMID: 33347700
-
Laboratory evaluation of fipronil against Periplaneta americana & Blattella germanica.Indian J Med Res. 2005 Jul;122(1):57-66. Indian J Med Res. 2005. PMID: 16106092
-
Evaluating Entomopathogenic Nematodes as Biocontrol Agents Against Two Major Cockroach Species, Blattella germanica and Periplaneta americana, in Antalya, Türkiye.Pathogens. 2025 Jul 1;14(7):655. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14070655. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40732702 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on the Insecticide Resistance of Three Species of Cockroaches (Blattodea: Blattidae) in Iran.J Econ Entomol. 2019 Feb 12;112(1):1-10. doi: 10.1093/jee/toy247. J Econ Entomol. 2019. PMID: 30137353 Review.
-
Contamination of Cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) by Medically Important Bacteriae: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Med Entomol. 2019 Oct 28;56(6):1534-1554. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjz095. J Med Entomol. 2019. PMID: 31219601
Cited by
-
Characterization in Potent Modulation on Voltage-Gated Na+ Current Exerted by Deltamethrin, a Pyrethroid Insecticide.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 25;23(23):14733. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314733. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal V. K., Tilak R., Gupta K. K. (2005). Efficacy of Synthetic Pyrethroid and Propoxur Aerosol in the Control of German Cockroaches (Dictyoptera: Blatellidae) in Cookhouses. J. Vector Borne Dis. 42, 117–121. - PubMed
-
- Ame J. M., Rivault C., Deneubourg J. L. (2004). Cockroach Aggregation Based on Strain Odour Recognition. Anim. Behav. 68 (4), 793–801. 10.1016/j.anbehav.2004.01.009 - DOI
-
- Bonnefoy X., Kampen H., Sweeney K.. Public health significance of urban pests. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. (2008) 54–84. ISBN 978-92-890-7188-8.
-
- Brenner R. J. (1995). “Economics and Medical Importance of German Cockroaches,” in Understanding and Controlling the German Cockroach. Editors Rust M. K., Owens J. M., Reierson D. A. (New York, USA: Oxford University Press; ), 77–92.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

