YciR, a Specific 3'-Phosphodiesterase, Plays a Role in the Pathogenesis of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli CFT073
- PMID: 35923408
- PMCID: PMC9339999
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.910906
YciR, a Specific 3'-Phosphodiesterase, Plays a Role in the Pathogenesis of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli CFT073
Abstract
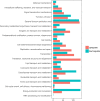
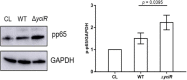
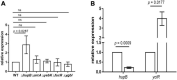
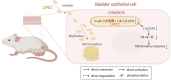
Urinary tract infections (UTIs), with the characteristics of recurrence and resistance to antibiotics due to misuse, remain a common health and economic issue for patients. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC), which is capable of evading the immune response by forming intracellular bacterial communities (IBCs) in the cytoplasm of bladder epithelial cells (BECs) after invasion, has been shown to be the prevailing cause of UTIs. Cyclic dimeric guanosine monophosphate (c-di-GMP) is a small molecule responsible for eliciting the innate immune response of the host only if it has not been degraded by some phosphodiesterases (PDEs), such as YciR. The relationship between YciR and c-di-GMP levels in UPEC is inconclusive. In this study, we investigated the gene expression profile of UPEC in BECs and identified yciR as an upregulated gene. Western blot revealed that YciR enhanced the virulence of UPEC by inhibiting the phosphorylation of NF-κB. The expression of yciR could be repressed by HupB in a directly binding manner. We identified YciR, a novel PDE, and defined its possible function in innate immune evasion. We also demonstrated that YciR is an HupB-dependent PDE that degrades c-di-GMP and that a low concentration of c-di-GMP might make NF-κB less phosphorylated, thereby reducing the host's pro-inflammatory response. This is the first time that YciR has been identified as a virulence factor in the pathogenesis of UPEC. These findings further increase our understanding of the pathogenesis of UPEC and provide a theoretical basis for further studies.
Keywords: cyclic dimeric guanosine monophosphate; phosphodiesterase; urinary tract infections; uropathogenic Escherichia coli; yciR.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Wang, Fan, Meng, Qian, Liu, Wei, Yuan, Du and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Enzymatically active and inactive phosphodiesterases and diguanylate cyclases are involved in regulation of Motility or sessility in Escherichia coli CFT073.mBio. 2012 Oct 9;3(5):e00307-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00307-12. mBio. 2012. PMID: 23047748 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Regulation of the Diguanylate Cyclase YaiC Reduces Production of Type 1 Fimbriae in a Pst Mutant of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli CFT073.J Bacteriol. 2017 Nov 14;199(24):e00168-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00168-17. Print 2017 Dec 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28924030 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Requirements of Escherichia coli in Intracellular Bacterial Communities during Urinary Tract Infection Pathogenesis.mBio. 2016 Apr 12;7(2):e00104-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00104-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27073089 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence factors of uropathogenic E. coli and their interaction with the host.Adv Microb Physiol. 2014;65:337-72. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Adv Microb Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25476769 Review.
-
Antibiotic Resistance Among Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Pol J Microbiol. 2019 Dec;68(4):403-415. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2019-048. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Pol J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31880885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Two-component system GrpP/GrpQ promotes pathogenicity of uropathogenic Escherichia coli CFT073 by upregulating type 1 fimbria.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 11;16(1):607. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-55982-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39799152 Free PMC article.
-
Low Expression of Phosphodiesterase 2 (PDE2A) Promotes the Progression by Regulating Mitochondrial Morphology and ATP Content and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2022 Dec 23;12(1):68. doi: 10.3390/cells12010068. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad I., Lamprokostopoulou A., Le Guyon S., Streck E., Barthel M., Peters V., et al. (2011). Complex c-di-GMP signaling networks mediate transition between virulence properties and biofilm formation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. PLoS One 6:e28351. 10.1371/journal.pone.0028351 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

