Estimating the burden of hepatitis B virus infection in Laos between 2020 and 2021: A cross-sectional seroprevalence survey
- PMID: 35923426
- PMCID: PMC9340506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101582
Estimating the burden of hepatitis B virus infection in Laos between 2020 and 2021: A cross-sectional seroprevalence survey
Abstract
Background: Laos is considered highly endemic for persistent infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV). To eliminate this burden, it has gradually implemented universal anti-hepatitis B immunisation of newborns over the past two decades.
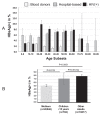
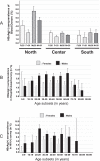
Methods: Using VIKIA® HBsAg, a rapid test for the qualitative detection of the HBV surface antigen, we conducted between Sep 1st, 2020 and Aug 31st, 2021 the largest prospective prevalence survey ever in Laos. This survey included blood donors (BD, n = 42,277), patients attending care in capital and provincial hospitals (n = 37,347) including attending mothers (n = 20,548), HIV-infected patients (n = 7439, recruited from 2009 to 2020), students from the Health Sciences University (n = 609), and outpatients (n = 350) coming for diagnosis at the Center Infectiology Lao-Christophe Mérieux in Vientiane. In total, 88,022 persons were tested, representing approximately 1.22% of the national population. To reach a reasonable estimate of HBsAg prevalence in Laos, we segmented the population according to three variables, age (≤20 years as a cut-off), sex, and geographical origin. BD values were used to estimate HBsAg prevalence in patients aged <20 while hospital survey prevalence was used to estimate the prevalence in those aged older than 20 years.
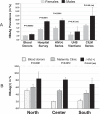
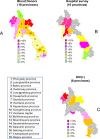
Findings: We observed an HBsAg seroprevalence ranging from 2.6% in blood donors to 8.0% in HIV-infected patients. In BD, men were significantly more at risk to be carriers than women (RR = 1.2, P = 0.00063). For BD, attending mothers, or HIV-infected patients, HBsAg was significantly more prevalent in northern Laos (5.1-8.4%) than in central (2.0-8.1%) or southern parts of the country (2.2-6.9%), thereby delineating a North-to-South gradient.
Interpretation: We considered that HBsAg prevalence probably ranges between 5.0% and 6.0% of the total population. Thus, we consider that Laos may no longer be highly endemic for chronic HBV infection but rather a country with intermediate endemicity.
Funding: The funding sources were the Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie, the French Government, the French Institute for Sustainable Development (IRD), and European Union's Horizon 2020 Marie Sklodowska-Curie Actions (MSCA) - Research and Innovation Staff Exchange - (RISE) under grant agreement N° 823935.
Keywords: Endemic country; Hepatitis B virus; Laos; Southeast Asia; Universal Immunization.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bell J, Nuzzo J. Global health security index: advancing collective action and accountability amid global crisis, 2021.
-
- Fund UNP. UNFPA Lao People's Democratic Republic. 2022.
-
- Organization WH. Global health observatory data repository. 2022.
-
- Hurie M, Mast E, Davis J. Horizontal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection to United States-born children of Hmong refugees. Pediatrics. 1992;89:269–273. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

