Targeting Impaired Nutrient Sensing via the Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Pathway With Therapeutic Compounds to Prevent or Treat Dementia: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35923682
- PMCID: PMC9341294
- DOI: 10.3389/fragi.2022.898853
Targeting Impaired Nutrient Sensing via the Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Pathway With Therapeutic Compounds to Prevent or Treat Dementia: A Systematic Review
Abstract
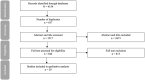
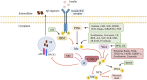
Background: Dementia is a global challenge with 10 million individuals being diagnosed every year. Currently, there are no established disease-modifying treatments for dementia. Impaired nutrient sensing has been implicated in the pathogenesis of dementia. Compounds that inhibit the glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3) pathway have been investigated as a possible treatment to attenuate the progression of the disease, particularly the suppression of the hyper-phosphorylation process of the tau protein. Aims: Systematically summarizing compounds which have been tested to inhibit the GSK3 pathway to treat cognitive impairment and dementia. Methods: PubMed, Embase and Web of Science databases were searched from inception until 28 July 2021 for articles published in English. Interventional animal studies inhibiting the GSK3 pathway in Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's dementia, Lewy body dementia, vascular dementia, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and normal cognitive ageing investigating the change in cognition as the outcome were included. The Systematic Review Centre for Laboratory animal Experimentation's risk of bias tool for animal studies was applied. Results: Out of 4,154 articles, 29 described compounds inhibiting the GSK3 pathway. All studies were based on animal models of MCI, AD or normal cognitive ageing. Thirteen out of 21 natural compounds and five out of nine synthetic compounds tested in MCI and dementia animal models showed an overall positive effect on cognition. No articles reported human studies. The risk of bias was largely unclear. Conclusion: Novel therapeutics involved in the modulation of the GSK3 nutrient sensing pathway have the potential to improve cognitive function. Overall, there is a clear lack of translation from animal models to humans.
Keywords: Alzheiemer’s disease; aged; ageing; cognition; dementia; glycogen syntase kinase 3; insulin resisitance.
Copyright © 2022 Matysek, Kimmantudawage, Feng and Maier.
Conflict of interest statement
AM is a scientific co-founder of Cognescence Ltd. and Immunidex Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repurposing Proteostasis-Modifying Drugs to Prevent or Treat Age-Related Dementia: A Systematic Review.Front Physiol. 2018 Oct 30;9:1520. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01520. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30425653 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment, Retainment, and Biomarkers of Response; A Pilot Trial of Lithium in Humans With Mild Cognitive Impairment.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Jun 28;12:163. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00163. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31316348 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating Alzheimer's Disease Progression Rates from Normal Cognition Through Mild Cognitive Impairment and Stages of Dementia.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2018;15(8):777-788. doi: 10.2174/1567205015666180119092427. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2018. PMID: 29357799 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction Models for Conversion From Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Apr 7;14:840386. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.840386. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35493941 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling in Alzheimer's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020 May;1867(5):118664. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118664. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32006534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad Rather M., Justin-Thenmozhi A., Manivasagam T., Saravanababu C., Guillemin G. J., Essa M. M. (2019). Asiatic Acid Attenuated Aluminum Chloride-Induced Tau Pathology, Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway in Wistar Rats. Neurotox. Res. 35, 955–968. 10.1007/s12640-019-9999-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akhtar A., Bishnoi M., Sah S. P. (2020). Sodium Orthovanadate Improves Learning and Memory in Intracerebroventricular-Streptozotocin Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease through Modulation of Brain Insulin Resistance Induced Tau Pathology. Brain Res. Bull. 164, 83–97. 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.08.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

