Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis Affects Quality of Life. A Case-Control Study
- PMID: 35923688
- PMCID: PMC9341334
- DOI: 10.2147/CCIDE.S369481
Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis Affects Quality of Life. A Case-Control Study
Abstract
Aim: To determine the impact of recurrent aphthous stomatitis on quality of life related to oral health, and then to determine the relationship between the observed impact and lesions characteristics.
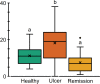
Methods: In this prospective case-control study (n=62), patients were divided into a healthy group (people with no history of ulcers) and recurrent aphthous stomatitis (people who had an active ulcer at study entry). The latter were also evaluated when the lesion disappeared (remission stage). We record the quality of life in all groups using the impact profile of oral health in its abbreviated Spanish version (OHIP-14SP). Finally, we correlate the clinical characteristics of the lesions with the levels of quality of life.
Results: All the lesions were of the minor morphological type. Most of the lesions were located on the lining mucosa, primarily on the lips. Patients report a lower quality of life during ulcer episodes compared to ulcer-free periods, and this impact is positively related to the number and size of lesions.
Conclusion: We concluded that recurrent aphthous stomatitis increased the negative effects of oral health on the quality of life of patients. The number and size of ulcers are responsible for this impact. Our results suggest that, if intervened locally, general relief of the condition could be achieved.
Keywords: aphthous ulcers; case-control studies; health-related quality of life; quality of life.
© 2022 Rivera et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in relation to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS): a preliminary within-subject study of quality of life, oral health impacts and personality profiles.J Oral Pathol Med. 2015 Apr;44(4):278-83. doi: 10.1111/jop.12232. Epub 2014 Aug 26. J Oral Pathol Med. 2015. PMID: 25154862
-
The association of recurrent aphthous stomatitis with general health and oral health related quality of life among dental students.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 15;14(4):254-261. eCollection 2022. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36161262 Free PMC article.
-
Irsogladine is effective for recurrent oral ulcers in patients with Behçet's disease : an open-label, single-centre study.Drugs R D. 2008;9(6):455-9. doi: 10.2165/0126839-200809060-00008. Drugs R D. 2008. PMID: 18989994 Clinical Trial.
-
The Clinical Use of Curcumin for the Treatment of Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1291:229-238. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-56153-6_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34331693
-
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis: clinical characteristics and associated systemic disorders.Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1997 Dec;16(4):278-83. doi: 10.1016/s1085-5629(97)80017-x. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1997. PMID: 9421219 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Oral Mucosal Diseases Using the Indonesian Version of the Chronic Oral Mucosal Disease Questionnaire-15 (COMDQ-15).Dent J (Basel). 2024 Aug 14;12(8):258. doi: 10.3390/dj12080258. Dent J (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195102 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Health and Nutraceutical Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 9;25(17):9733. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179733. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis with oral roflumilast, a multicenter observational study.Int J Dermatol. 2024 Dec;63(12):e390-e396. doi: 10.1111/ijd.17478. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Int J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39301981 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Nov;27(11):6345-6356. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05273-y. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 37798535
-
Assessing the Impact of Recurrent Aphthous Ulcer on Oral Health-Related Quality of Life.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025 Jun;17(Suppl 2):S1733-S1736. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_293_25. Epub 2025 Jun 18. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025. PMID: 40655647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nature. Latest research and news by subject: quality of life; 2019. Avaialble from: https://www.nature.com/subjects/quality-of-life. Accessed November 22, 2019.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

