Novel etodolac derivatives as eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF2K) inhibitors for targeted cancer therapy
- PMID: 35923718
- PMCID: PMC9298183
- DOI: 10.1039/d2md00105e
Novel etodolac derivatives as eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF2K) inhibitors for targeted cancer therapy
Abstract
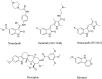
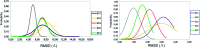
Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF2K) has been shown to be an important molecular driver of tumorigenesis and validated as a potential novel molecular target in various solid cancers including triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Therefore, there has been significant interest in identifying novel inhibitors of eEF2K for the development of targeted therapeutics and clinical translation. Herein, we investigated the effects of indole ring containing derivatives of etodolac, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) drug, as potential eEF2K inhibitors and we designed and synthesized seven novel compounds with a pyrano[3,4-b] indole core structure. We evaluated the eEF2K inhibitory activity of seven of these novel compounds using in silico molecular modeling and in vitro studies in TNBC cell lines. We identified two novel compounds (EC1 and EC7) with significant in vitro activity in inhibiting eEF2K in TNBC cells. In conclusion, our studies indicate that pyrano[3,4-b] indole scaffold containing compounds demonstrate marked eEF2K inhibitory activity and they may be used as eEF2K inhibitors for the development of eEF2K-targeted therapeutics.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Novel inhibitors of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase: In silico, synthesis and in vitro studies.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Nov;116:105296. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105296. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34488125
-
MicroRNA 603 acts as a tumor suppressor and inhibits triple-negative breast cancer tumorigenesis by targeting elongation factor 2 kinase.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 14;8(7):11641-11658. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14264. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28036267 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1 regulates expression of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase and promotes proliferation, invasion and tumorgenesis of human triple negative breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 29;7(13):16619-35. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7672. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26918606 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase (eEF2K) signaling in tumor and microenvironment as a novel molecular target.J Mol Med (Berl). 2020 Jun;98(6):775-787. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-01917-8. Epub 2020 May 7. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32377852 Review.
-
Targeting eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF2K) with small-molecule inhibitors for cancer therapy.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Oct;29(10):104155. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.104155. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 39214495 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advancements in Refashioning of NSAIDs and their Derivatives as Anticancer Candidates.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(16):1217-1239. doi: 10.2174/0113816128304230240327044201. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38584541 Review.
-
Impact of silencing eEF2K expression on the malignant properties of chordoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Apr;50(4):3011-3022. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08257-z. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36652154
-
Synthesis, in silico and bio-evaluation studies of new isothiocyanate derivatives with respect to COX inhibition and H2S release profiles.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Oct 24. doi: 10.1039/d4md00495g. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39507615 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of Boron in the Modulation of Gut Microbiota Composition: An In Vivo Pilot Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 6;17(10):1334. doi: 10.3390/ph17101334. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458975 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and In Silico Evaluation of Piperazine-Substituted 2,3-Dichloro-5,8-dihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone Derivatives as Potential PARP-1 Inhibitors.ACS Omega. 2024 Sep 10;9(38):39733-39742. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c04915. eCollection 2024 Sep 24. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39346823 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

