Reactivity-based chemical-genetic study of protein kinases
- PMID: 35923719
- PMCID: PMC9298188
- DOI: 10.1039/d1md00389e
Reactivity-based chemical-genetic study of protein kinases
Abstract
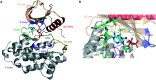
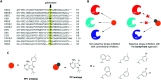
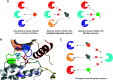
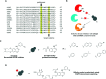
The human protein kinase superfamily comprises over 500 members that operate in nearly every signal transduction pathway and regulate essential cellular processes. Deciphering the functional roles of protein kinases with small-molecule inhibitors is essential to enhance our understanding of cell signaling and to facilitate the development of new therapies. However, it is rather challenging to identify selective kinase inhibitors because of the conserved nature of the ATP binding site. A number of chemical-genetic approaches have been developed during the past two decades to enable selective chemical perturbation of the activity of individual kinases. Herein, we review the development and application of chemical-genetic strategies that feature the use of covalent inhibitors targeting cysteine residues to dissect the cellular functions of protein kinases.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


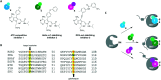
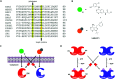



Similar articles
-
A historical overview of protein kinases and their targeted small molecule inhibitors.Pharmacol Res. 2015 Oct;100:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.07.010. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Pharmacol Res. 2015. PMID: 26207888 Review.
-
Chemical genetic strategy for targeting protein kinases based on covalent complementarity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Sep 13;108(37):15046-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111239108. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21852571 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Recognition of FDA-Approved Small Molecule Protein Kinase Drugs in Protein Kinases.Molecules. 2022 Oct 21;27(20):7124. doi: 10.3390/molecules27207124. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296718 Free PMC article.
-
A Chemical-Genetic Approach to Generate Selective Covalent Inhibitors of Protein Kinases.ACS Chem Biol. 2017 Jun 16;12(6):1499-1503. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b01083. Epub 2017 May 8. ACS Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28459525 Free PMC article.
-
Developing irreversible inhibitors of the protein kinase cysteinome.Chem Biol. 2013 Feb 21;20(2):146-59. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.12.006. Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23438744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

