Major cardiac surgery with recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein replacement in hemophilia B: a case report
- PMID: 35923771
- PMCID: PMC9340359
- DOI: 10.1177/20406207221104595
Major cardiac surgery with recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein replacement in hemophilia B: a case report
Abstract
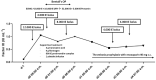
The introduction of extended factor IX (FIX) products has significantly facilitated the treatment of hemophilia B patients. However, optimal perioperative management remains a topic of hot debate, particularly in surgeries with high bleeding risk. For the first time, we report here a patient with mild hemophilia B and degenerative aneurysms of aortic root and ascending aorta undergoing elective Bentall's operation with full cardiopulmonary bypass, who was successfully managed with eftrenonacog alfa (Alprolix®), a recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein (rFIXFc). rFIXFc could safely be monitored using the Pathromtin SL aPTT-reagent. No significant bleeding was noted intraoperatively despite systemic heparinization as well as postoperatively. Higher doses of rFIXFc were inevitable to reach target FIX levels intraoperatively, whereas in the post-surgery setting stable FIX concentrations were maintained with only few rFIXFc injections facilitating fast wound healing and remobilization of the patient.
Keywords: Bentall’s operation; case report; eftrenonacog alfa.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: CF reports research grant, reimbursement for attending symposium, and consulting fees from Sobi. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eftrenonacog Alfa: A Review in Haemophilia B.Drugs. 2023 Jun;83(9):807-818. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01868-7. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37081241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world usage and effectiveness of recombinant factor VIII/factor IX Fc in hemophilia A/B: final data from the 24-month, prospective, noninterventional PREVENT study in Germany.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2024 Jun 21;8(5):102482. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2024.102482. eCollection 2024 Jul. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2024. PMID: 39101128 Free PMC article.
-
Measurements of eftrenonacog alfa by 19 different combinations reagents/instrument: A single-centre study.Haemophilia. 2020 May;26(3):543-552. doi: 10.1111/hae.14003. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Haemophilia. 2020. PMID: 32314511
-
Eftrenonacog Alfa: A Review in Haemophilia B.Drugs. 2017 Jul;77(11):1235-1246. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0778-1. Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28646426 Clinical Trial.
-
Continuous prophylaxis with recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein and conventional recombinant factor IX products: comparisons of efficacy and weekly factor consumption.J Med Econ. 2017 Apr;20(4):337-344. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2016.1265973. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Med Econ. 2017. PMID: 27885871
Cited by
-
Is it safe to perform coronary artery bypass grafting surgery in patients with hemophilia? A case series of four patients.Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2025 Apr 30;33(2):251-256. doi: 10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2025.25800. eCollection 2025 Apr. Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2025. PMID: 40575061 Free PMC article.
-
Modern Treatment of Valvulopathies in Patients with Congenital Hemophilia.Life (Basel). 2024 Mar 7;14(3):354. doi: 10.3390/life14030354. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38541679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant factor IX Fc for major surgery in hemophilia B: factor IX plasma activity levels and effective hemostasis.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023 Aug 7;7(6):102169. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2023.102169. eCollection 2023 Aug. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 37694269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giangrande P. Haemophilia B: Christmas disease. Exp Opin Pharmacother 2005; 6: 1517–1524. - PubMed
-
- Panicker J, Warrier I, Thomas R, et al.. The overall effectiveness of prophylaxis in severe haemophilia. Haemophilia 2003; 9: 272–278. - PubMed
-
- Neufeld EJ, Solimeno L, Quon D, et al.. Perioperative management of haemophilia B: a critical appraisal of the evidence and current practices. Haemophilia 2017; 23: 821–831. - PubMed
-
- Powell JS, Pasi KJ, Ragni MV, et al.. Phase 3 study of recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein in hemophilia B. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 2313–2323. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources