Hematogenous dissemination of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Leptospira in a short-term murine model of infection
- PMID: 35923802
- PMCID: PMC9339599
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.917962
Hematogenous dissemination of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Leptospira in a short-term murine model of infection
Abstract
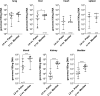
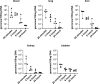
Leptospirosis is an emerging zoonosis caused by pathogenic Leptospira spp. Because rodents are natural hosts of Leptospira, rodent models of pathogenesis have been limited, but are valuable to understand infection in reservoir animals even in the absence of disease. Mouse models of infection provide advantages due to genetic tractability, so developing murine models of Leptospira infection is crucial for further understanding the biology of this organism. Previously our laboratory developed a short-term murine model of Borrelia burgdorferi hematogenous dissemination to investigate the role of adhesion proteins on bacterial survival and dissemination within a host. Here we adapt this model to Leptospira. C3H/HeJ mice are anesthetized, inoculated intravenously, and then bacteria are allowed to circulate for up to twenty-four hours. Mice are euthanized, perfused with saline, and tissues are harvested for culture and DNA purification. Bacterial burdens are determined by quantitative PCR. Reproducible burdens of bacteria were found in tissues upon inoculation with pathogens and non-pathogens, demonstrating the utility of this model to probe different Leptospira species and strains. Pathogenic L. interrogans has a significantly higher burden in blood, liver, kidney, and bladder at one-hour post-inoculation when compared to non-pathogenic L. biflexa. Colonization of the kidney is essential to the life cycle of pathogenic Leptospira in nature. Measurable burdens of non-pathogenic L. biflexa were found in numerous organs and live leptospires were recovered from blood samples for at least three hours post-inoculation, contrary to the previous belief that non-pathogenic leptospires are rapidly cleared. This short-term murine model of Leptospira hematogenous dissemination will allow for the interrogation of virulence factors potentially important for tissue colonization and evasion of host defenses, and represents a novel animal model for investigating determinants of Leptospira infection.
Keywords: Leptospira; adhesion; infectious disease; murine model; pathogenic factors; tropism.
Copyright © 2022 Surdel, Anderson, Hahn and Coburn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adler B., Cameron C., Haake D., Hartskeerl R., Ellis W., Levitt P., et al. (2014). Leptospira and leptospirosis (New York: Springer; ).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

