Screening of ferroptosis-related genes in sepsis-induced liver failure and analysis of immune correlation
- PMID: 35923893
- PMCID: PMC9341447
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13757
Screening of ferroptosis-related genes in sepsis-induced liver failure and analysis of immune correlation
Abstract
Purpose: Sepsis-induced liver failure is a kind of liver injury with a high mortality, and ferroptosis plays a key role in this disease. Our research aims to screen ferroptosis-related genes in sepsis-induced liver failure as targeted therapy for patients with liver failure.
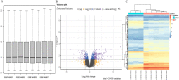
Methods: Using the limma software, we analyzed the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the GSE60088 dataset downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Clusterprofiler was applied for enrichment analysis of DEGs enrichment function. Then, the ferroptosis-related genes of the mice in the FerrDb database were crossed with DEGs. Sepsis mice model were prepared by cecal ligation and perforation (CLP). ALT and AST in the serum of mice were measured using detection kit. The pathological changes of the liver tissues in mice were observed by hematoxylin-eosin (H & E) staining. We detected the apoptosis of mice liver tissues using TUNEL. The expression of Hmox1, Epas1, Sirt1, Slc3a2, Jun, Plin2 and Zfp36 were detected by qRT-PCR.
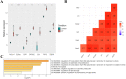
Results: DEGs analysis showed 136 up-regulated and 45 down-regulated DEGs. Meanwhile, we found that the up-regulated DEGs were enriched in pathways including the cytokine biosynthesis process while the down-regulated DEGs were enriched in pathways such as organic hydroxy compound metabolic process. In this study, seven genes (Hmox1, Epas1, Sirt1, Slc3a2, Jun, Plin2 and Zfp36) were obtained through the intersection of FerrDb database and DEGs. However, immune infiltration analysis revealed that ferroptosis-related genes may promote the development of liver failure through B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. Finally, it was confirmed by the construction of septic liver failure mice model that ferroptosis-related genes of Hmox1, Slc3a2, Jun and Zfp36 were significantly correlated with liver failure and were highly expressed.
Conclusion: The identification of ferroptosis-related genes Hmox1, Slc3a2, Jun and Zfp36 in the present study contribute to our understanding of the molecular mechanism of sepsis-induced liver failure, and provide candidate targets for the diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Keywords: Animal experimental verification; Ferroptosis-related gene; Immunoassay; Liver failure; Sepsis.
©2022 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Chen W, Chen M, Zhao Z, Weng Q, Song J, Fang S, Wu X, Wang H, Zhang D, Yang W, Wang Z, Xu M, Ji J. ZFP36 binds with PRC1 to inhibit tumor growth and increase 5-Fu chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. 2020;7:126. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00126. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

