Research Progress on the Mechanism of Sepsis Induced Myocardial Injury
- PMID: 35923903
- PMCID: PMC9342248
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S374117
Research Progress on the Mechanism of Sepsis Induced Myocardial Injury
Abstract
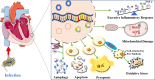
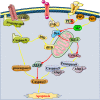
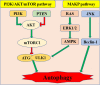
Sepsis is an abnormal condition with multiple organ dysfunctions caused by the uncontrolled infection response and one of the major diseases that seriously hang over global human health. Besides, sepsis is characterized by high morbidity and mortality, especially in intensive care unit (ICU). Among the numerous subsequent organ injuries of sepsis, myocardial injury is one of the most common complications and the main cause of death in septic patients. To better manage septic inpatients, it is necessary to understand the specific mechanisms of sepsis induced myocardial injury (SIMI). Therefore, this review will elucidate the pathophysiology of SIMI from the following certain mechanisms: apoptosis, mitochondrial damage, autophagy, excessive inflammatory response, oxidative stress and pyroptosis, and outline current therapeutic strategies and potential approaches in SIMI.
Keywords: mechanism; sepsis induced myocardial injury; signaling pathway.
© 2022 Bi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Shankar-Hari M, Harrison DA, Rubenfeld GD, Rowan K. Epidemiology of sepsis and septic shock in critical care units: comparison between sepsis-2 and sepsis-3 populations using a national critical care database. Br J Anaesth. 2017;119(4):626–636. - PubMed
-
- Kaukonen KM, Bailey M, Suzuki S, Pilcher D, Bellomo R. Mortality related to severe sepsis and septic shock among critically ill patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000–2012. JAMA. 2014;311(13):1308–1316. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources