Brain-Inspired Affective Empathy Computational Model and Its Application on Altruistic Rescue Task
- PMID: 35923916
- PMCID: PMC9341284
- DOI: 10.3389/fncom.2022.784967
Brain-Inspired Affective Empathy Computational Model and Its Application on Altruistic Rescue Task
Abstract
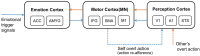
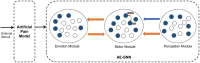
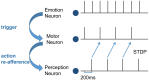
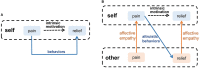
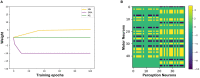
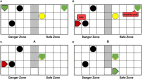
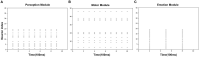
Affective empathy is an indispensable ability for humans and other species' harmonious social lives, motivating altruistic behavior, such as consolation and aid-giving. How to build an affective empathy computational model has attracted extensive attention in recent years. Most affective empathy models focus on the recognition and simulation of facial expressions or emotional speech of humans, namely Affective Computing. However, these studies lack the guidance of neural mechanisms of affective empathy. From a neuroscience perspective, affective empathy is formed gradually during the individual development process: experiencing own emotion-forming the corresponding Mirror Neuron System (MNS)-understanding the emotions of others through the mirror mechanism. Inspired by this neural mechanism, we constructed a brain-inspired affective empathy computational model, this model contains two submodels: (1) We designed an Artificial Pain Model inspired by the Free Energy Principle (FEP) to the simulate pain generation process in living organisms. (2) We build an affective empathy spiking neural network (AE-SNN) that simulates the mirror mechanism of MNS and has self-other differentiation ability. We apply the brain-inspired affective empathy computational model to the pain empathy and altruistic rescue task to achieve the rescue of companions by intelligent agents. To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first one to reproduce the emergence process of mirror neurons and anti-mirror neurons in the SNN field. Compared with traditional affective empathy computational models, our model is more biologically plausible, and it provides a new perspective for achieving artificial affective empathy, which has special potential for the social robots field in the future.
Keywords: Artificial Pain; affective empathy; altruistic behavior; mirror neuron system; self-awareness; spiking neural network.
Copyright © 2022 Feng, Zeng and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
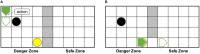
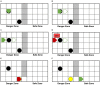
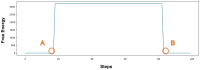
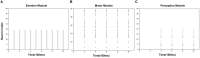
Similar articles
-
A brain-inspired robot pain model based on a spiking neural network.Front Neurorobot. 2022 Dec 20;16:1025338. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2022.1025338. eCollection 2022. Front Neurorobot. 2022. PMID: 36605522 Free PMC article.
-
Intergroup empathy: Enhanced neural resonance for ingroup facial emotion in a shared neural production-perception network.Neuroimage. 2019 Jul 1;194:182-190. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.03.048. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 30914383
-
Mirror neuron and theory of mind mechanisms involved in face-to-face interactions: a functional magnetic resonance imaging approach to empathy.J Cogn Neurosci. 2007 Aug;19(8):1354-72. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2007.19.8.1354. J Cogn Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17651008
-
A developmental perspective on the neural bases of human empathy.Infant Behav Dev. 2017 Aug;48(Pt A):5-12. doi: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2015.11.006. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Infant Behav Dev. 2017. PMID: 26995647 Review.
-
[Empathy and mirror neurons. A view on contemporary neuropsychological empathy research].Prax Kinderpsychol Kinderpsychiatr. 2012;61(5):322-35. doi: 10.13109/prkk.2012.61.5.322. Prax Kinderpsychol Kinderpsychiatr. 2012. PMID: 22957393 Review. German.
Cited by
-
BrainCog: A spiking neural network based, brain-inspired cognitive intelligence engine for brain-inspired AI and brain simulation.Patterns (N Y). 2023 Jul 6;4(8):100789. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2023.100789. eCollection 2023 Aug 11. Patterns (N Y). 2023. PMID: 37602224 Free PMC article.
-
Bonding with nature: a validation of the dispositional empathy with nature scale in Italy.Front Psychol. 2025 Feb 28;16:1388798. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1388798. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40092674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asada M. (2015). Towards artificial empathy. Int. J. Soc. Robotics 7, 19–33. 10.1007/s12369-014-0253-z - DOI
-
- Asada M. (2019). Artificial pain may induce empathy, morality, and ethics in the conscious mind of robots. Philosophies 4, 38–30. 10.3390/philosophies4030038 - DOI
-
- Broom D. M. (2001). Evolution of pain. Vlaams Diergeneeskd Tijdschr. 70, 17–21.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

