Targeted Nipple Areola Complex Reinnervation: Technical Considerations and Surgical Efficiency in Implant-based Breast Reconstruction
- PMID: 35923997
- PMCID: PMC9325332
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004420
Targeted Nipple Areola Complex Reinnervation: Technical Considerations and Surgical Efficiency in Implant-based Breast Reconstruction
Abstract
Background: Despite promising pilot study results, adoption of neurotization of immediate implant-based reconstructions has not occurred.
Methods: For surgeons interested in adopting breast reinnervation techniques, we present ways to overcome initial barriers by decreasing operative time and maximizing chances of sensory recovery.
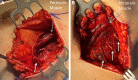
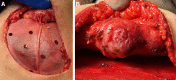
Results: We discuss the combined experience at two academic teaching hospitals, where neurotization of both immediate tissue expander cases and direct-to-implant reconstructions are performed through varying mastectomy incisions.
Conclusion: Initial barriers can be overcome by shortening operative time and providing an individualized reinnervation approach that aims to increase the chance of meaningful sensation.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures
References
-
- Jaspars JJ, Posma AN, van Immerseel AA, et al. The cutaneous innervation of the female breast and nipple-areola complex: implications for surgery. Br J Plast Surg. 1997;50:249–259. - PubMed
-
- Yueh JH, Houlihan MJ, Slavin SA, et al. Nipple-sparing mastectomy: evaluation of patient satisfaction, aesthetic results, and sensation. Ann Plast Surg. 2009;62:586–590. - PubMed
-
- Djohan R, Gage E, Gatherwright J, et al. Patient satisfaction following nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction: an 8-year outcome study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125:818–829. - PubMed
-
- Peled AW, Duralde E, Foster RD, et al. Patient-reported outcomes and satisfaction after total skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate expander-implant reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2014;72 (Suppl 1):S48–S52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
