Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Diseases: Theories, Applications, and Mechanisms
- PMID: 35924053
- PMCID: PMC9340222
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.917975
Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Diseases: Theories, Applications, and Mechanisms
Abstract
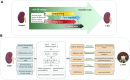
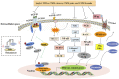
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common and progressive disease that has become a major public health problem on a global scale. Renal fibrosis is a common feature in the pathogenesis of CKD, which is mainly related to the excessive accumulation and deposition of extracellular matrix caused by various inflammatory factors. No ideal treatment has yet been established. In recent years, based on the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) theory of CKD and its molecular mechanism, clinical evidence or experimental studies have confirmed that a variety of Chinese materia medica (CMM) and their effective components can delay the progress of CKD. TCM believes that the pathogenesis of CKD is the deficiency in the root and excess in the branch, and the deficiency and excess are always accompanied by the disease. The strategies of TCM in treating CKD are mainly based on invigorating Qi, tonifying the kidneys, promoting blood circulation, removing stasis, eliminating heat and dampness, removing turbidity, and eliminating edema, and these effects are multitargeted and multifunctional. This review attempts to summarize the theories and treatment strategies of TCM in the treatment of CKD and presents the efficacy and mechanisms of several CMMs supported by clinical evidence or experimental studies. In addition, the relationship between the macroscopic of TCM and the microscopic of modern medicine and the problems faced in further research were also discussed.
Keywords: Chinese materia medica; chronic kidney disease; intervention mechanism; reinforcing deficiency and purging excess; renal fibrosis; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Feng, Li, Yang, Shi, Xuan, Yin and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Pathogenesis of ferroptosis on chronic kidney disease and traditional Chinese medicine intervention: a review].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 May;49(10):2629-2639. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240111.701. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38812163 Review. Chinese.
-
Data Mining-Based Analysis of Chinese Medicinal Herb Formulae in Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jan 24;2020:9719872. doi: 10.1155/2020/9719872. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32047530 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Chinese Yang/Qi-Invigorating Tonic Botanical Drugs/Herbal Formulations in Ameliorating Chronic Kidney Disease by Enhancing Mitochondrial Function.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 24;12:622498. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.622498. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34248614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[New thoughts on material basis and mechanism of Yin-tonifying traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of diabetes mellitus and its complications].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Feb;45(3):531-538. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190826.502. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32237510 Review. Chinese.
-
[Efficiency of benazepril combined with wind dispelling and dampness removing chinese herbs on stage 3 chronic kidney disease with wind-dampness syndrome: a prospective study].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012 Mar;32(3):311-6. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22686073 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Study on the mechanism of hirudin multi target delaying renal function decline in chronic kidney disease based on the "gut-kidney axis" theory.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Oct;397(10):7951-7962. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02888-6. Epub 2024 May 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38758227 Free PMC article.
-
N1F(Improved-Nephropathy 1 Formula) Ameliorates Renal Interstitial Fibrosis via Inhibiting Extracellular Matrix Deposition and Regulating the FGF23/P38MAPK/Wnt Pathway.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Jun;82(2):927-943. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01244-6. Epub 2024 May 9. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38722471
-
Shenshuaikang enema restores the intestinal barrier and microbiota-gut-kidney axis balance to alleviate chronic kidney disease via NF-κB pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 21;15:1453668. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1453668. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39906395 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the therapeutic potential of natural products in Alzheimer's disease: insights from in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1601712. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1601712. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40626308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of trimethylamine N-oxide in disease pathogenesis and the therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1592524. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1592524. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40777990 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cai H., Su S., Li Y., Zeng H., Zhu Z., Guo J., et al. (2018). Protective Effects of Salvia Miltiorrhiza on Adenine-Induced Chronic Renal Failure by Regulating the Metabolic Profiling and Modulating the NADPH oxidase/ROS/ERK and TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 212, 153–165. 10.1016/j.jep.2017.09.021 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

