Kangfuxiaoyanshuan alleviates uterine inflammation and adhesion via inhibiting NF-κB p65 and TGF-β/MMP-2 signaling pathway in pelvic inflammatory disease rats
- PMID: 35924054
- PMCID: PMC9340273
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.894149
Kangfuxiaoyanshuan alleviates uterine inflammation and adhesion via inhibiting NF-κB p65 and TGF-β/MMP-2 signaling pathway in pelvic inflammatory disease rats
Abstract
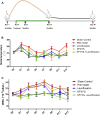
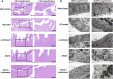
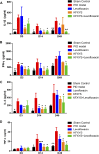
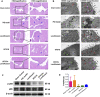
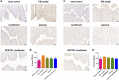
Background and aims: Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is infection-induced inflammation of the female upper reproductive tract that results in high fever, ectopic pregnancy, infertility, and varying degrees of chronic pelvic pain. Recent clinical studies have shown that Kangfuxiaoyanshuan (KFXYS), a Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) formulation, may short the course of the disease and reduce the occurrence of PID sequelae, but its pharmacological action and potential mechanism have not been fully elucidated. Here, we aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects and mechanism of KFXYS in rats with PID. Materials and Methods: A PID rat model was constructed through endometrial mechanical injury and pathogen infection. The rectal temperature was measured during the 14-days course of treatment, and the white blood cell (WBC) count in the blood and the levels of cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-4, TNF-α) in the serum were evaluated by ELISA. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining was performed to analyze pathological changes, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to observe ultrastructural changes. The p-p65/p65 protein expression was evaluated by western blotting and the levels of MMP-2 and TGF-β in adhesion tissues were assessed by immunohistochemistry. Results: KFXYS lowered the rectal temperature and the WBC counts in the blood in the acute stage of PID and alleviated inflammatory cell infiltration of the uterus, especially when combined with levofloxacin. KFXYS significantly decreased the levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-4) and adhesion-related factors (TNF-α) and protected the ultrastructure of endometrial epithelial cells. Mechanistically, KFXYS inhibited the NF-κB activation by decreasing phosphorylation of p65, thus the alleviation of inflammation further reduced the expression of TGF-β and MMP-2, and inhibited the occurrence of uterine adhesions. Conclusion: These results revealed that KFXYS alleviated pelvic inflammation and effectively inhibits inflammation-associated adhesion, which indicated the potential role of KFXYS for treatment of PID and the prevention of PID sequelae.
Keywords: MMP-2; NF-κB; TGF-β; anti-inflammation; kangfuxiaoyanshuan; pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Copyright © 2022 Fan, Liu, Zhang, Li, Zong and Bai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pen Yan Jing Tablets Alleviates Pelvic Inflammatory Disease by Inhibiting Akt/NF-κB Pathway.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Sep 4;20(11):1386-1398. doi: 10.7150/ijms.87433. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37790843 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-proliferation and anti-inflammation effects of corilagin in rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Feb 10;284:114791. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114791. Epub 2021 Oct 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34737112
-
Ozone therapy ameliorates inflammation and endometrial injury in rats with pelvic inflammatory disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Nov;107:1418-1425. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.137. Epub 2018 Sep 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30257358
-
Identifying the clinical presentations, progression, and sequela of pelvic inflammatory disease through physiological, histological and ultrastructural evaluation of a rat animal model.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Dec;9(23):1710. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-3345. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 35071404 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Kangfuxiaomi suppository on pelvic inflammatory disease in rats.J Reprod Immunol. 2023 Dec;160:104154. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2023.104154. Epub 2023 Sep 20. J Reprod Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37774536
Cited by
-
Exploration into the Mechanism of Yiyi Baijiang Decoction Attenuating Chronic Pelvic Inflammation Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification.Biochem Genet. 2025 Aug;63(4):2879-2892. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10843-0. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 38856955
-
Roles of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and their associated molecules in the pathogenesis of keloids: a comprehensive review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 25;15:1444653. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1444653. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39654616 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

