N6-Methyladenosine Reader YTHDF2 Enhances Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis through Mediating circ_SFMBT2 Degradation
- PMID: 35924072
- PMCID: PMC9308553
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1087622
N6-Methyladenosine Reader YTHDF2 Enhances Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis through Mediating circ_SFMBT2 Degradation
Abstract
Objective: circ_SFMBT2 was reported to facilitate malignant progression in various cancers, but its function in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has not been fully uncovered. This study aimed to investigate the effects of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation of circ_SFMBT2 (circ_0017628) on non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and its underlying mechanisms.
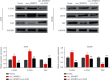
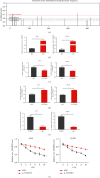
Methods: Paired tumor and noncancerous tissues from NSCLC patients were surgically collected from January 2020 to March 2021 in our hospital. The levels of circ_SFMBT2 and LATS2 in NSCLC and human bronchial epithelial cells were assayed with qRT-PCR. Overexpression or silencing of circ_SFMBT2, LATS2, or YTHDF2 was performed in the NSCLC cells. CCK-8, colony-forming, and transwell assays were performed to analyze cell proliferation, viability, and migration, respectively. Meanwhile, the expression of MMP-9, E-cadherin, vimentin, and the Hippo/YAP pathway components was examined by western blotting. The m6A enrichment in circ_SFMBT2 was verified using methylated RNA immunoprecipitation, and interaction between circ_SFMBT2 and YTHDF2 was assessed by RNA pull-down and immunoprecipitation assays.
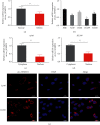
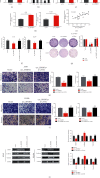
Results: Both circ_SFMBT2 and LATS2 were lowly expressed in NSCLC cells and tissues. A positive correlation of circ_SFMBT2 with LATS2 was identified, and circ_SFMBT2 was localized predominantly in the cytoplasm. circ_SFMBT2 overexpression negatively regulated cell proliferation, viability, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition while promoting the Hippo/YAP pathway activation. Notably, knockdown of LATS2 effectively abrogated the inhibitory effects of circ_SFMBT2 overexpression on NSCLC cell malignancies. Besides, m6A was specifically enriched in circ_SFMBT2, and circ_SFMBT2 could bind to YTHDF2. Silencing of YTHDF2 led to an increase in circ_SFMBT2 expression while inhibiting the malignancy of cancer cells.
Conclusion: Our results showed that YTHDF2 could facilitate NSCLC cell proliferation and metastasis via the Hippo/YAP pathway activation by mediating circ_SFMBT2 degradation.
Copyright © 2022 Jing Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel R. L. Miller K. D. Jemal A. Cancer statistics. A Cancer Journal for Clinicians . 2020;70(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Chen W. Zheng R. Baade P. D. Cancer statistics in China. Journal of European Economy . 2016;66(2):115–132. - PubMed
-
- Torre L. A. Siegel R. L. Jemal A. Lung cancer statistics. Advances in Experimental Medicine & Biology . 2016;893:1–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
