The Key Role of microRNAs in Initiation and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35924150
- PMCID: PMC9341471
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.950374
The Key Role of microRNAs in Initiation and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
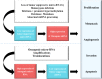
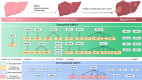
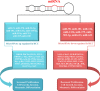
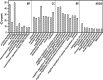
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the main type of primary liver malignancy and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a type of non-coding RNA that regulates gene expression mainly on post-transcriptional level has a confirmed and important role in numerous biological process. By regulating specific target genes, miRNA can act as oncogene or tumor suppressor. Recent evidence has indicated that the deregulation of miR-NAs is closely associated with the clinical pathological features of HCC. However, the precise regulatory mechanism of each miRNA and its targets in HCC has yet to be illuminated. This study demonstrates that both oncogenic and tumor suppressive miRNAs are crucial in the formation and development of HCC. miRNAs influence biological behavior including proliferation, invasion, metastasis and apoptosis by targeting critical genes. Here, we summarize current knowledge about the expression profile and function of miRNAs in HCC and discuss the potential for miRNA-based therapy for HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; microRNA; oncogene; therapy; tumor suppressor.
Copyright © 2022 Khan, Zhang, Zhang, Hayat, Ren, Nasir, Fawad and Bai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of microRNA-regulated protein interaction network reveals the tumor suppressive role of microRNA-149 in human hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting AKT-mTOR pathway.Mol Cancer. 2014 Nov 26;13:253. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-253. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25424347 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-342-3p is a potent tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2021 Jan;74(1):122-134. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.039. Epub 2020 Jul 30. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 32738449
-
MicroRNA-504 functions as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibiting Frizzled-7-mediated-Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Nov;107:754-762. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.150. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30142536
-
miRNAs inspirations in hepatocellular carcinoma: Detrimental and favorable aspects of key performers.Pathol Res Pract. 2022 May;233:153886. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.153886. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Pathol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35405621 Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Circular RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2018 Apr 12;9(9):1548-1559. doi: 10.7150/jca.24566. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29760792 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation and Optimization of MiR-375 Nano-Vector Using Two Novel Chitosan-Coated Nano-Structured Lipid Carriers as Gene Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Apr 3;16(4):494. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040494. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38675155 Free PMC article.
-
Current therapies and progress in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 26;14:1327055. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1327055. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38469246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-coding RNA 02298 Promotes the Malignancy of HCC by Targeting the miR-28-5p/CCDC6 Pathway.Biochem Genet. 2024 Dec;62(6):4967-4986. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10662-9. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 38381357
-
MicroRNA-204-5p Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting the Regulator of G Protein Signaling 20.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Nov 6;6(12):1817-1828. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00114. eCollection 2023 Dec 8. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 38093845 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking-related dysregulation of plasma circulating microRNAs: the Rotterdam study.Hum Genomics. 2023 Jul 10;17(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s40246-023-00504-5. Hum Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37430296 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

