Comparing DESI-MSI and MALDI-MSI Mediated Spatial Metabolomics and Their Applications in Cancer Studies
- PMID: 35924152
- PMCID: PMC9340374
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.891018
Comparing DESI-MSI and MALDI-MSI Mediated Spatial Metabolomics and Their Applications in Cancer Studies
Abstract
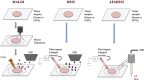
Metabolic heterogeneity of cancer contributes significantly to its poor treatment outcomes and prognosis. As a result, studies continue to focus on identifying new biomarkers and metabolic vulnerabilities, both of which depend on the understanding of altered metabolism in cancer. In the recent decades, the rise of mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) enables the in situ detection of large numbers of small molecules in tissues. Therefore, researchers look to using MSI-mediated spatial metabolomics to further study the altered metabolites in cancer patients. In this review, we examined the two most commonly used spatial metabolomics techniques, MALDI-MSI and DESI-MSI, and some recent highlights of their applications in cancer studies. We also described AFADESI-MSI as a recent variation from the DESI-MSI and compare it with the two major techniques. Specifically, we discussed spatial metabolomics results in four types of heterogeneous malignancies, including breast cancer, esophageal cancer, glioblastoma and lung cancer. Multiple studies have effectively classified cancer tissue subtypes using altered metabolites information. In addition, distribution trends of key metabolites such as fatty acids, high-energy phosphate compounds, and antioxidants were identified. Therefore, while the visualization of finer distribution details requires further improvement of MSI techniques, past studies have suggested spatial metabolomics to be a promising direction to study the complexity of cancer pathophysiology.
Keywords: DESI-MSI; MALDI-MSI; breast cancer; cancer heterogeneity; esophageal cancer; glioblastoma; lung cancer; spatial metabolomics.
Copyright © 2022 He, Pu, Wang, Zhang, Tang and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in mass spectrometry imaging for spatial cancer metabolomics.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2024 Mar-Apr;43(2):235-268. doi: 10.1002/mas.21804. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2024. PMID: 36065601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial-resolved metabolomics reveals tissue-specific metabolic reprogramming in diabetic nephropathy by using mass spectrometry imaging.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Nov;11(11):3665-3677. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.013. Epub 2021 May 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34900545 Free PMC article.
-
In situ metabolomics in nephrotoxicity of aristolochic acids based on air flow-assisted desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Jun;10(6):1083-1093. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.12.004. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 32642414 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial metabolomics principles and application to cancer research.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2023 Oct;76:102362. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2023.102362. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37413787 Review.
-
Spatial metabolomics in mental disorders and traditional Chinese medicine: a review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 31;16:1449639. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1449639. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39959419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid Metabolism Heterogeneity and Crosstalk with Mitochondria Functions Drive Breast Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 19;14(24):6267. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246267. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Use of Patient-Derived Organoids in the Study of Molecular Metabolic Adaptation in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 29;25(19):10503. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910503. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Imaging Mass Spectrometry for Biomedical and Clinical Research.Trends Analyt Chem. 2023 Dec;169:117344. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.117344. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Trends Analyt Chem. 2023. PMID: 38045023 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging and spatially resolved mass spectrometry applications in nephrology.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025 Jun;21(6):399-416. doi: 10.1038/s41581-025-00946-1. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40148534 Review.
-
DESI-TQ-MS imaging for ex vivo brain biodistribution assessment: evaluation of LBT-999, a ligand of the dopamine transporter (DAT).EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024 Aug 27;9(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s41181-024-00289-5. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024. PMID: 39192050 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

