Impairment of RAD17 Functions by miR-506-3p as a Novel Synthetic Lethal Approach Targeting DNA Repair Pathways in Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 35924161
- PMCID: PMC9340372
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.923508
Impairment of RAD17 Functions by miR-506-3p as a Novel Synthetic Lethal Approach Targeting DNA Repair Pathways in Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
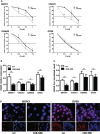
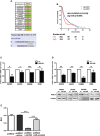
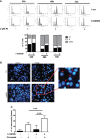
Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) remains the most lethal gynecological cancer and development of chemo-resistance is a major factor in disease relapse. Homologous recombination (HR) is a critical pathway for DNA double strand break repair and its deficiency is associated to a better response to DNA damage-inducing agents. Strategies to inhibit HR-mediated DNA repair is a clinical need to improve patients' outcome. MicroRNA (miRNAs) affect most of cellular processes including response to cancer treatment. We previously showed that miR-506-3p targets RAD51, an essential HR component. In this study we demonstrated that: i) another HR component, RAD17, is also a direct target of miR-506-3p and that it is involved in mediating miR-506-3p phenotypic effects; ii) the impairment of miR-506-3p binding to RAD17 3' UTR reverted the miR-506-3p induced platinum sensitization; iii) miR-506-3p/RAD17 axis reduces the ability of EOC cell to sense DNA damage, abrogates the G2/M cell cycle checkpoint thus delaying the G2/M cell cycle arrest likely allowing the entry into mitosis of heavily DNA-damaged cells with a consequent mitotic catastrophe; iv) RAD17 expression, regulated by miR-506-3p, is synthetically lethal with inhibitors of cell cycle checkpoint kinases Chk1 and Wee1 in platinum resistant cell line. Overall miR-506-3p expression may recapitulate a BRCAness phenotype sensitizing EOC cells to chemotherapy and helping in selecting patients susceptible to DNA damaging drugs in combination with new small molecules targeting DNA-damage repair pathway.
Keywords: ChrXq27.3 miRNA cluster; DNA damage and repair; RAD17; cell cycle checkpoint inhibitors; miR-506-3p; ovarian cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Bagnoli, Nicoletti, Valitutti, Rizzo, Napoli, Montalvão De Azevedo, Tomassetti and Mezzanzanica.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
AP4 suppresses DNA damage, chromosomal instability and senescence via inducing MDC1/Mediator of DNA damage Checkpoint 1 and repressing MIR22HG/miR-22-3p.Mol Cancer. 2022 May 27;21(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01581-1. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35624466 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 20 regulates Rad17 stability, checkpoint kinase 1 phosphorylation and DNA repair by homologous recombination.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 15;289(33):22739-22748. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.550459. Epub 2014 Jun 12. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24923443 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-222-3p/GNAI2/AKT axis inhibits epithelial ovarian cancer cell growth and associates with good overall survival.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80633-80654. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13017. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27811362 Free PMC article.
-
ChrXq27.3 miRNA cluster functions in cancer development.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 25;40(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01910-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33766100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platinum Resistance in Ovarian Cancer: Role of DNA Repair.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jan 20;11(1):119. doi: 10.3390/cancers11010119. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30669514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel players in the development of chemoresistance in ovarian cancer: ovarian cancer stem cells, non-coding RNA and nuclear receptors.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 Feb 28;7:6. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2023.152. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38434767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of microRNA-506 in cancer treatment: mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 3;15:1524763. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1524763. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40248198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of RAD17 as a candidate cancer predisposition gene in families with histories of pancreatic and breast cancers.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jun 13;24(1):723. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12442-z. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38872153 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the complexity of HRD assessment in ovarian cancer by combining genomic and functional approaches: translational analyses of MITO16-MaNGO-OV-2 trial.ESMO Open. 2025 Jan;10(1):104091. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.104091. Epub 2025 Jan 3. ESMO Open. 2025. PMID: 39754985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discovery (2022) 12:31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

