IL-17A Increases Doxorubicin Efficacy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35924165
- PMCID: PMC9340269
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.928474
IL-17A Increases Doxorubicin Efficacy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
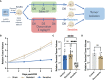
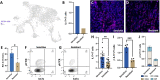
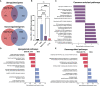
Due to lack of targetable receptors and intertumoral heterogeneity, triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains particularly difficult to treat. Doxorubicin (DOX) is typically used as nonselective neoadjuvant chemotherapy, but the diversity of treatment efficacy remains unclear. Comparable to variability in clinical response, an experimental model of TNBC using a 4T1 syngeneic mouse model was found to elicit a differential response to a seven-day treatment regimen of DOX. Single-cell RNA sequencing identified an increase in T cells in tumors that responded to DOX treatment compared to tumors that continued to grow uninhibited. Additionally, compared to resistant tumors, DOX sensitive tumors contained significantly more CD4 T helper cells (339%), γδ T cells (727%), Naïve T cells (278%), and activated CD8 T cells (130%). Furthermore, transcriptional profiles of tumor infiltrated T cells in DOX responsive tumors revealed decreased exhaustion, increased chemokine/cytokine expression, and increased activation and cytotoxic activity. γδ T cell derived IL-17A was identified to be highly abundant in the sensitive tumor microenvironment. IL-17A was also found to directly increase sensitivity of TNBC cells in combination with DOX treatment. In TNBC tumors sensitive to DOX, increased IL-17A levels lead to a direct effect on cancer cell responsiveness and chronic stimulation of tumor infiltrated T cells leading to improved chemotherapeutic efficacy. IL-17A's role as a chemosensitive cytokine in TNBC may offer new opportunities for treating chemoresistant breast tumors and other cancer types.
Keywords: 4T1; IL-17A; chemoresistance; doxorubicin; single cell RNA seq; triple negative breast cancer; γδ T cells.
Copyright © 2022 Hum, Sebastian, Martin, Rios-Arce, Gilmore, Gravano, Wheeler, Coleman and Loots.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Doxorubicin-polyglycerol-nanodiamond conjugate is a cytostatic agent that evades chemoresistance and reverses cancer-induced immunosuppression in triple-negative breast cancer.J Nanobiotechnology. 2019 Oct 17;17(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12951-019-0541-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019. PMID: 31623629 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cell depletion therapy targets IL-17A-expressing mammary carcinomas.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 7;10(1):13343. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70231-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32770025 Free PMC article.
-
Rhein potentiates doxorubicin in treating triple negative breast cancer by inhibiting cancer-associated fibroblasts.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 May;223:116139. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116139. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38499109
-
Tumor Microenvironment-Triggered Charge Reversal Polymetformin-Based Nanosystem Co-Delivered Doxorubicin and IL-12 Cytokine Gene for Chemo-Gene Combination Therapy on Metastatic Breast Cancer.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Oct 14;12(41):45873-45890. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c14405. Epub 2020 Sep 29. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32924511
-
Novel miRNA Targets and Therapies in the Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Microenvironment: An Emerging Hope for a Challenging Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 24;21(23):8905. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238905. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33255471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The modulation of immune cell death in connection to microRNAs and natural products.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 20;15:1425602. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425602. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39759512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PNKP targeting engages the autophagic machinery through STING and STAT3 to potentiate ferroptosis and chemotherapy in TNBC.Redox Biol. 2025 Jul 22;86:103775. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103775. Online ahead of print. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40743845 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular interactions between metformin and D-limonene inhibit proliferation and promote apoptosis in breast and liver cancer cells.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 May 6;24(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04453-x. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 38711049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asselain B, Barlow W, Bartlett J, Bergh J, Bergsten-Nordström E, Bliss J, et al. . Long-Term Outcomes for Neoadjuvant Versus Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Early Breast Cancer: Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data From Ten Randomised Trials. Lancet Oncol (2018) 19(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30777-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mackey JR, Pieńkowski T, Crown J, Sadeghi S, Martin M, Chan A, et al. . Long-Term Outcomes After Adjuvant Treatment of Sequential Versus Combination Docetaxel With Doxorubicin and Cyclophosphamide in Node-Positive Breast Cancer: BCIRG-005 Randomized Trial. Ann Oncol (2016) 27(6):1041–7. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw098 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Geisler S, Lønning PE, Aas T, Johnsen H, Fluge O, Haugen DF, et al. . Influence of TP53 Gene Alterations and c-erbB-2 Expression on the Response to Treatment With Doxorubicin in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer. Cancer Res (2001) 61(6):2505–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

