Subliminal Emotional Faces Elicit Predominantly Right-Lateralized Amygdala Activation: A Systematic Meta-Analysis of fMRI Studies
- PMID: 35924231
- PMCID: PMC9339677
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.868366
Subliminal Emotional Faces Elicit Predominantly Right-Lateralized Amygdala Activation: A Systematic Meta-Analysis of fMRI Studies
Abstract
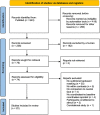
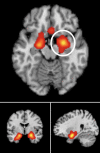
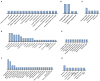
Prior research suggests that conscious face processing occurs preferentially in right hemisphere occipito-parietal regions. However, less is known about brain regions associated with non-conscious processing of faces, and whether a right-hemispheric dominance persists in line with specific affective responses. We aim to review the neural responses systematically, quantitatively, and qualitatively underlying subliminal face processing. PubMed was searched for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) publications assessing subliminal emotional face stimuli up to March 2022. Activation Likelihood Estimation (ALE) meta-analyses and narrative reviews were conducted on all studies that met ALE requirements. Risk of bias was assessed using the AXIS tool. In a meta-analysis of all 22 eligible studies (merging clinical and non-clinical populations, whole brain and region of interest analyses), bilateral amygdala activation was reported in the left (x = -19.2, y = 1.5, z = -17.1) in 59% of studies, and in the right (x = 24.4, y = -1.7, z = -17.4) in 68% of studies. In a second meta-analysis of non-clinical participants only (n = 18), bilateral amygdala was again reported in the left (x = -18, y = 3.9, z = -18.4) and right (x = 22.8, y = -0.9, z = -17.4) in 56% of studies for both clusters. In a final meta-analysis of whole-brain studies only (n=14), bilateral amygdala was also reported in the left (x = -20.2, y = 2.9, z = -17.2) in 64% of studies, and right (x = 24.2, y = -0.7, z = -17.8) in 71% of studies. The findings suggest that non-consciously detected emotional faces may influence amygdala activation, especially right-lateralized (a higher percentage of convergence in studies), which are integral for pre-conscious affect and long-term memory processing.
Keywords: Activation Likelihood Estimation; amygdala; emotional faces; parahippocampal gyrus; subliminal.
Copyright © 2022 Dahlén, Schofield, Schiöth and Brooks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neural correlates of successful emotional episodic encoding and retrieval: An SDM meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies.Neuropsychologia. 2020 Jun;143:107495. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2020.107495. Epub 2020 May 13. Neuropsychologia. 2020. PMID: 32416099
-
Exposure to subliminal arousing stimuli induces robust activation in the amygdala, hippocampus, anterior cingulate, insular cortex and primary visual cortex: a systematic meta-analysis of fMRI studies.Neuroimage. 2012 Feb 1;59(3):2962-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.077. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22001789
-
Visual cortical regions show sufficient test-retest reliability while salience regions are unreliable during emotional face processing.Neuroimage. 2020 Oct 15;220:117077. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117077. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32574806 Free PMC article.
-
Functional atlas of emotional faces processing: a voxel-based meta-analysis of 105 functional magnetic resonance imaging studies.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2009 Nov;34(6):418-32. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19949718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural functional correlates of emotional processing in patients with first-episode psychoses: an activation likelihood estimation (ALE) meta-analysis.Arch Ital Biol. 2018 Jul 1;156(1-2):1-11. doi: 10.12871/00039829201811. Arch Ital Biol. 2018. PMID: 30039831 Review.
Cited by
-
Vivid imagery of objects primes perception of subliminal spatial information.Neurosci Conscious. 2025 Aug 11;2025(1):niaf026. doi: 10.1093/nc/niaf026. eCollection 2025. Neurosci Conscious. 2025. PMID: 40799212 Free PMC article.
-
Amygdala fMRI-A Critical Appraisal of the Extant Literature.Neurosci Insights. 2024 Aug 13;19:26331055241270591. doi: 10.1177/26331055241270591. eCollection 2024. Neurosci Insights. 2024. PMID: 39148643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass-univariate analysis of scalp ERPs reveals large effects of gaze fixation location during face processing that only weakly interact with face emotional expression.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 9;13(1):17022. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44355-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37813928 Free PMC article.
-
Altered intrinsic brain activity and functional connectivity in COVID-19 hospitalized patients at 6-month follow-up.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Aug 8;23(1):521. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08331-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37553613 Free PMC article.
-
Fear perception as a function of hemisphere- and time-specific dynamics in the medial temporal lobes.Commun Biol. 2025 Jul 25;8(1):1105. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08542-6. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40715793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brooks S. J., Savov V., Allzén E., Benedict C., Fredriksson R., Schiöth H. B. (2012). Exposure to subliminal arousing stimuli induces robust activation in the amygdala, hippocampus, anterior cingulate, insular cortex and primary visual cortex: a systematic meta-analysis of fMRI studies. NeuroImage 59, 2962–2973. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.077 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

