Sciatic-Vagal Nerve Stimulation by Electroacupuncture Alleviates Inflammatory Arthritis in Lyme Disease-Susceptible C3H Mice
- PMID: 35924250
- PMCID: PMC9342905
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.930287
Sciatic-Vagal Nerve Stimulation by Electroacupuncture Alleviates Inflammatory Arthritis in Lyme Disease-Susceptible C3H Mice
Abstract
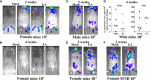
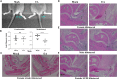
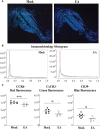
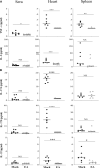
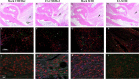
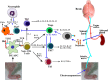
Lyme disease is caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, and the pathogenesis of the disease is complex with both bacterial and host factors contributing to inflammatory responses. Lyme disease affects different organs including joints and results in arthritis. Immune responses stimulated by B. burgdorferi through toll-like receptors cause infiltration of leukocytes, which produce inflammatory cytokines and facilitate spirochete clearance. However, arthritic manifestations and chronic fatigue syndrome-like symptoms persist long after completion of antibiotic treatment regimens in a significant number of patients. To counter the effects of inflammation, treatment by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hydroxychloroquine, or synovectomy to eradicate inflammatory arthritis in the involved joint could be employed; however, they often have long-term consequences. Acupuncture has been used for a long time in Asian medicine to diminish pain during various ailments, but the effects and its mechanism are just beginning to be explored. Control of inflammation by neuronal stimulation has been exploited as a systemic therapeutic intervention to arrest inflammatory processes. Our objective was to determine whether activation of the sciatic-vagal network by electroacupuncture on ST36 acupoint, which is used to control systemic inflammation in experimental models of infectious disorders such as endotoxemia, can also alleviate Lyme arthritis symptoms in mice. This aim was further strengthened by the reports that sciatic-vagal neuronal network stimulation can lead to dopamine production in the adrenal medulla and moderate the production of inflammatory factors. We first assessed whether electroacupuncture affects spirochete colonization to attenuate Lyme arthritis. Interestingly, bioluminescent B. burgdorferi burden detected by live imaging and qPCR were similar in electroacupuncture- and mock-treated mice, while electroacupuncture induced a lasting anti-inflammatory effect on mice. Despite the discontinuation of treatment at 2 weeks, the simultaneous decrease in neutrophils in the joints and inflammatory cytokine levels throughout the body at 4 weeks suggests a systemic and persistent effect of electroacupuncture that attenuates Lyme arthritis. Our results suggest that electroacupuncture-mediated anti-inflammatory responses could offer promising healthcare benefits in patients suffering from long-term Lyme disease manifestations.
Keywords: Borrelia burgdorferi; Lyme arthritis; electroacupuncture; inflammation; sciatic nerve; vagus nerve.
Copyright © 2022 Akoolo, Djokic, Rocha, Ulloa and Parveen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Burgdorfer W, Barbour AG, Hayes SF, Benach JL, Grunwaldt E, Davis JP. Lyme Disease-a Tick-Borne Spirochetosis? Science (1982) 216(4552):1317–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

