Bibliometrics analysis on the research status and trends of adult-onset Still's disease: 1921-2021
- PMID: 35924251
- PMCID: PMC9339616
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.950641
Bibliometrics analysis on the research status and trends of adult-onset Still's disease: 1921-2021
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this research is to discuss the research status, hotspots, frontiers and development trends in the field of adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) based on bibliometrics and visual analysis by CiteSpace software.
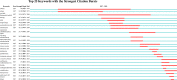
Methods: The relevant research articles on AOSD from 1921 to 2021 were retrieved from the Scopus database. CiteSpace software was used to form a visual knowledge map and conduct analysis for the countries/regions, journals, authors, keywords, clusters, research hotspots and frontiers of the included articles.
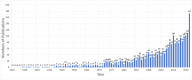
Results: There were 2,373 articles included, and the number of articles published during 1921-2021 is increasing. The country with the highest number of articles published was Japan (355, 14.96%), followed by the United States (329, 13.86%) and France (215, 9.06%). The author with the highest number of publications is Ansell, Barbara M. (30, 1.26%), and the author with the highest co-citation frequency is Yamaguchi, Masaya (703). Clinical Rheumatology is the journal with the highest publication frequency. The top five cluster groups were "joint", "differential diagnosis", "prednisolone", "methotrexate" and "macrophage activation syndrome". The diagnosis, treatment and pathogenesis of AOSD form the main research fields, and prognosis and complications are the research hotspots and trends.
Conclusions: The global research field in AOSD has expanded in the past 100 years. The complications and new pathogenesis of AOSD are hotspots in this field and need further study in the future.
Keywords: Still’s disease; adult-onset; bibliometrics [MeSH]; epidemiology; scopus; trends.
Copyright © 2022 Qin, Sun, Gao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

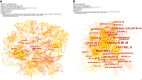


Similar articles
-
Bibliometrics analysis on the research status and trends of small bowel adenocarcinoma: 1923-2023.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 21;14:1407315. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1407315. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39234397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometrics and Visual Analysis of Adult-onset Still Disease (1976-2020).Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 15;10:884780. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.884780. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35784223 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and comorbidities in adult-onset Still's disease using a large US administrative claims database.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Jul 1;59(7):1725-1733. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez622. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 31965185 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of Interleukin-18 as a Diagnostic Biomarker to Differentiate Adult-Onset Still's Disease With/Without Macrophage Activation Syndrome From Other Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 8;12:750114. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.750114. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34691064 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review on adult onset Still's disease.J Autoimmun. 2018 Sep;93:24-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.07.018. Epub 2018 Aug 1. J Autoimmun. 2018. PMID: 30077425 Review.
Cited by
-
Research trends in vascular chips from 2012 to 2022: a bibliometrix and visualized analysis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 11;12:1409467. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1409467. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39055344 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Trends in Psoriasis and Metabolic Syndrome.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 Feb 9;17:365-382. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S446966. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38352064 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage bibliometric study and visualization in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025 Aug 5;20(1):322. doi: 10.1186/s13019-025-03563-y. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025. PMID: 40764610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proposal of a new diagnostic algorithm for adult-onset Still's disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Apr;42(4):1125-1135. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06509-8. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36694091
-
Bibliometric analysis and visualized study of research on autophagy in ischemic stroke.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 4;14:1232114. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1232114. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37731738 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

