Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion in Lung Transplantation
- PMID: 35924535
- PMCID: PMC9358162
- DOI: 10.5090/jcs.22.056
Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion in Lung Transplantation
Abstract
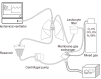
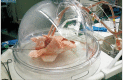
Ex vivo lung perfusion (EVLP) is a technique that enables active metabolism of the lung by creating an environment similar to that inside the body, even though the explanted lungs are outside the body. The EVLP system enables the use of lung grafts that do not satisfy the acceptance criteria for lung transplantation (LTx) by making it possible to evaluate the function of the lung grafts and repair lungs in poor condition, thereby reducing the waiting time of patients requiring LTx and consequently mortality.
Keywords: Donor pool; Ex vivo lung perfusion; Lung transplantation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes of marginal donors for lung transplantation after ex vivo lung perfusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020 Feb;159(2):720-730.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2019.07.087. Epub 2019 Aug 25. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 31548078
-
Early results in transplantation of initially rejected donor lungs after ex vivo lung perfusion: a case-control study.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014 Jan;45(1):40-4; discussion 44-5. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezt250. Epub 2013 May 10. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014. PMID: 23666375
-
Ten year follow-up of lung transplantations using initially rejected donor lungs after reconditioning using ex vivo lung perfusion.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019 Jul 1;14(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13019-019-0948-1. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31262311 Free PMC article.
-
First experience with ex vivo lung perfusion for initially discarded donor lungs in the Netherlands: a single-centre study.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019 May 1;55(5):920-926. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezy373. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019. PMID: 30496383
-
Ex vivo lung perfusion: a potential platform for molecular diagnosis and ex vivo organ repair.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Jun;10(Suppl 16):S1871-S1883. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.04.119. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30026974 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact and relevance of techniques and fluids on lung injury in machine perfusion of lungs.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 6;15:1358153. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1358153. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38510260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Ex-Vivo Lung Perfusion for Planned Left Single-Lung Transplant.Ann Thorac Surg Short Rep. 2024 Aug 6;3(1):247-249. doi: 10.1016/j.atssr.2024.07.025. eCollection 2025 Mar. Ann Thorac Surg Short Rep. 2024. PMID: 40098856 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

