Redescription, deposition of life-cycle stage specimens of Sarcocystis bovifelis Heydorn, Gestrich, Mehlhorn and Rommel, 1975, and amendment to Sarcocystis hirsuta Moulé, 1888
- PMID: 35924738
- PMCID: PMC11010579
- DOI: 10.1017/S0031182022001044
Redescription, deposition of life-cycle stage specimens of Sarcocystis bovifelis Heydorn, Gestrich, Mehlhorn and Rommel, 1975, and amendment to Sarcocystis hirsuta Moulé, 1888
Abstract
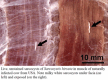
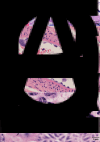
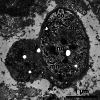
There is considerable debate concerning the life cycles and taxonomy of Sarcocystis species in cattle. Of the 8 species of Sarcocystis named from cattle, 2 (Sarcocystis cruzi and Sarcocystis heydorni) are morphologically distinctive because their sarcocysts are microscopic and the sarcocyst wall is thin (<0.5 μm thick). The sarcocysts of the remaining species (Sarcocystis hirsuta, Sarcocystis hominis, Sarcocystis bovini, Sarcocystis bovifelis, Sarcocystis sinensis, Sarcocystis rommeli) have thick (5–8 μm) walls indistinguishable by light microscopy, alone. To provide needed clarity, I herein review the history, nomenclature and life cycle of S. bovifelis (originally named by Heydorn and associates from Germany), redescribe it and deposit specimens of its various life-cycle stages at a museum for future reference. I also provide means to distinguish this parasite from S. hirsuta. Cats are the definitive hosts for both S. bovifelis and S. hirsuta. The sarcocysts of S. bovifelis are microscopic, its sarcocyst wall is type 10g, it has 2 schizogonic stages in blood vessels and sarcocysts are formed between 25 and 30 days post-inoculation in striated muscles, but not in the heart. Sporulated oocysts are 17.1 × 12.7 μm and sporocysts are 12.8 × 8.4 μm. The sarcocysts of Sarcocystis hirsuta are macroscopic, up to 7 mm long, its wall is type 18. Nothing is known of the development of S. hirsuta in cattle tissues and in cat intestine. Size of its oocysts and sporocysts is uncertain.
Keywords: Amendment; Sarcocystis bovifelis; Sarcocystis hirsuta; cat; cattle; history; life cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares there are no conflicts of interests.
Figures
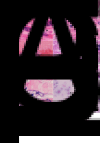




Similar articles
-
Sarcocystis cruzi (Hasselmann, 1923) Wenyon, 1926: redescription, molecular characterization and deposition of life cycle stages specimens in the Smithsonian Museum.Parasitology. 2023 Nov;150(13):1192-1206. doi: 10.1017/S003118202300094X. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Parasitology. 2023. PMID: 37850439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphological and molecular characterization of a Sarcocystis bovifelis-like sarcocyst in American beef.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Dec 28;17(1):543. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06628-4. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 39732700 Free PMC article.
-
The resurrection of a species: Sarcocystis bovifelis Heydorn et al., 1975 is distinct from the current Sarcocystis hirsuta in cattle and morphologically indistinguishable from Sarcocystis sinensis in water buffaloes.Parasitol Res. 2016 Jan;115(1):1-21. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4785-4. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Parasitol Res. 2016. PMID: 26462803 Review.
-
Molecular characterisation of Sarcocystis bovifelis, Sarcocystis bovini n. sp., Sarcocystis hirsuta and Sarcocystis cruzi from cattle (Bos taurus) and Sarcocystis sinensis from water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis).Parasitol Res. 2016 Apr;115(4):1473-92. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4881-5. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Parasitol Res. 2016. PMID: 26677095
-
Sarcocystis heydorni, n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) with cattle (Bos taurus) and human (Homo sapiens) cycle.Parasitol Res. 2015 Nov;114(11):4143-7. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4645-2. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Parasitol Res. 2015. PMID: 26243573
Cited by
-
Sarcocystis species: molecular identification and seroprevalence in water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis).BMC Vet Res. 2025 Jul 22;21(1):482. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04933-3. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40696429 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcocystis cruzi (Hasselmann, 1923) Wenyon, 1926: redescription, molecular characterization and deposition of life cycle stages specimens in the Smithsonian Museum.Parasitology. 2023 Nov;150(13):1192-1206. doi: 10.1017/S003118202300094X. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Parasitology. 2023. PMID: 37850439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of Sarcocystis hominis, Sarcocystis bovifelis, Sarcocystis cruzi, Sarcocystis hirsuta and Sarcocystis sigmoideus sp. nov. in carcasses affected by bovine eosinophilic myositis.Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2024 Jan 19;34:e00220. doi: 10.1016/j.fawpar.2024.e00220. eCollection 2024 Mar. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2024. PMID: 38313347 Free PMC article.
-
The Distribution of Sarcocsytis Species Described by Ungulates-Canids Life Cycle in Intestines of Small Predators of the Family Mustelidae.Acta Parasitol. 2024 Mar;69(1):747-758. doi: 10.1007/s11686-024-00814-1. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Acta Parasitol. 2024. PMID: 38413556
-
Morphological and molecular characterization of a Sarcocystis bovifelis-like sarcocyst in American beef.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Dec 28;17(1):543. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06628-4. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 39732700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boch J, Laupheimer KE and Erber M (1978) Drei sarkosporidienarten bei schlachtrindern in süddeutschland. Berliner und Münchener Tierärztliche Wochenschrift 91, 426–431. - PubMed
-
- Böttner A, Charleston WAG and Hopcroft D (1987a) The structure and the identity of macroscopically visible Sarcocystis cysts in cattle. Veterinary Parasitology 24, 35–45. - PubMed
-
- Böttner A, Charleston WAG, Pomroy WE and Rommel M (1987b) The prevalence and identity of Sarcocystis in beef cattle in New Zealand. Veterinary Parasitology 24, 157–168. - PubMed
-
- Dubey JP (1982) Development of the ox–cat cycle of Sarcocystis hirsuta. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington 49, 295–304.
-
- Dubey JP (1983a) Microgametogony of Sarcocystis hirsuta in the intestine of the cat. Parasitology 86, 7–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

