Coupling to short linear motifs creates versatile PME-1 activities in PP2A holoenzyme demethylation and inhibition
- PMID: 35924897
- PMCID: PMC9398451
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.79736
Coupling to short linear motifs creates versatile PME-1 activities in PP2A holoenzyme demethylation and inhibition
Abstract
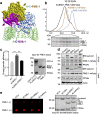
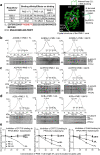
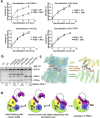
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) holoenzymes target broad substrates by recognizing short motifs via regulatory subunits. PP2A methylesterase 1 (PME-1) is a cancer-promoting enzyme and undergoes methylesterase activation upon binding to the PP2A core enzyme. Here, we showed that PME-1 readily demethylates different families of PP2A holoenzymes and blocks substrate recognition in vitro. The high-resolution cryoelectron microscopy structure of a PP2A-B56 holoenzyme-PME-1 complex reveals that PME-1 disordered regions, including a substrate-mimicking motif, tether to the B56 regulatory subunit at remote sites. They occupy the holoenzyme substrate-binding groove and allow large structural shifts in both holoenzyme and PME-1 to enable multipartite contacts at structured cores to activate the methylesterase. B56 interface mutations selectively block PME-1 activity toward PP2A-B56 holoenzymes and affect the methylation of a fraction of total cellular PP2A. The B56 interface mutations allow us to uncover B56-specific PME-1 functions in p53 signaling. Our studies reveal multiple mechanisms of PME-1 in suppressing holoenzyme functions and versatile PME-1 activities derived from coupling substrate-mimicking motifs to dynamic structured cores.
Keywords: E. coli; P53; PME-1; biochemistry; chemical biology; demethylation; molecular biophysics; protein phosphatase 2A; short linear motifs; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
YL, VB, MR, CW, AB, VY, YI, SS, IN, YX No competing interests declared
Figures








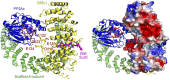




Similar articles
-
Emerging Roles of B56 Phosphorylation and Binding Motif in PP2A-B56 Holoenzyme Biological Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 10;25(6):3185. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063185. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural mechanism of demethylation and inactivation of protein phosphatase 2A.Cell. 2008 Apr 4;133(1):154-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.041. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18394995
-
A dynamic charge-charge interaction modulates PP2A:B56 substrate recruitment.Elife. 2020 Mar 20;9:e55966. doi: 10.7554/eLife.55966. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32195664 Free PMC article.
-
Two Distinct Mechanisms of PP2A Regulation by Methylesterase PME-1 Are Both Essential for Mouse Development.FASEB J. 2025 May 15;39(9):e70554. doi: 10.1096/fj.202402617RR. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40326231
-
Regulation and role of the PP2A-B56 holoenzyme family in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023 Sep;1878(5):188953. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188953. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37437699 Review.
Cited by
-
GlPRMT5 inhibits GlPP2C1 via symmetric dimethylation and regulates the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in Ganoderma lucidum.Commun Biol. 2024 Feb 28;7(1):241. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-05942-y. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38418849 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of B56 Phosphorylation and Binding Motif in PP2A-B56 Holoenzyme Biological Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 10;25(6):3185. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063185. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipolysis of bone marrow adipocytes fuels bone.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022 Sep;18(9):522. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00723-1. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35821109 No abstract available.
-
PME-1 sensitizes glioblastoma cells to oxidative stress-induced cell death by attenuating PP2A-B55α-mediated inactivation of MAPKAPK2-RIPK1 signaling.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jul 27;9(1):265. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01572-1. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37500619 Free PMC article.
-
Extended regulation interface coupled to the allosteric network and disease mutations in the PP2A-B56δ holoenzyme.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 5:2023.03.09.530109. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.09.530109. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37066309 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung L-W, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica. Section D, Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachovchin DA, Mohr JT, Speers AE, Wang C, Berlin JM, Spicer TP, Fernandez-Vega V, Chase P, Hodder PS, Schürer SC, Nomura DK, Rosen H, Fu GC, Cravatt BF. Academic cross-fertilization by public screening yields a remarkable class of protein phosphatase methylesterase-1 inhibitors. PNAS. 2011;108:6811–6816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015248108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

