Pandemic 1918 Influenza Virus Does Not Cause Lethal Infection in Rhesus or Cynomolgus Macaques
- PMID: 35924920
- PMCID: PMC9400491
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00728-22
Pandemic 1918 Influenza Virus Does Not Cause Lethal Infection in Rhesus or Cynomolgus Macaques
Abstract
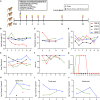
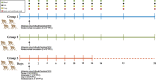
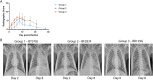
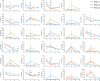
The 1918 H1N1 influenza pandemic was among the most severe in history, taking the lives of approximately 50 million people worldwide, and novel prophylactic vaccines are urgently needed to prevent another pandemic. Given that macaques are physiologically relevant preclinical models of human immunology that have advanced the clinical treatment of infectious diseases, a lethal pandemic influenza challenge model would provide a stringent platform for testing new influenza vaccine concepts. To this end, we infected rhesus macaques and Mauritian cynomolgus macaques with highly pathogenic 1918 H1N1 influenza virus and assessed pathogenesis and disease severity. Despite infection with a high dose of 1918 influenza delivered via multiple routes, rhesus macaques demonstrated minimal signs of disease, with only intermittent viral shedding. Cynomolgus macaques infected via intrabronchial instillation demonstrated mild symptoms, with disease severity depending on the infection dose. Cynomolgus macaques infected with a high dose of 1918 influenza delivered via multiple routes experienced moderate disease characterized by consistent viral shedding, pulmonary infiltrates, and elevated inflammatory cytokine levels. However, 1918 influenza was uniformly nonlethal in these two species, demonstrating that this isolate is insufficiently pathogenic in rhesus and Mauritian cynomolgus macaques to support testing novel prophylactic influenza approaches where protection from severe disease combined with a lethal outcome is desired as a highly stringent indication of vaccine efficacy. IMPORTANCE The world remains at risk of an influenza pandemic, and the development of new therapeutic and preventative modalities is critically important for minimizing human death and suffering during the next influenza pandemic. Animal models are central to the development of new therapies and vaccine approaches. In particular, nonhuman primates like rhesus and cynomolgus macaques are highly relevant preclinical models given their physiological and immunological similarities to humans. Unfortunately, there remains a scarcity of macaque models of pandemic influenza with which to test novel antiviral modalities. Here, we demonstrate that even at the highest doses tested, 1918 influenza was not lethal in these two macaque species, suggesting that they are not ideal for the development and testing of novel pandemic influenza-specific vaccines and therapies. Therefore, other physiologically relevant nonhuman primate models of pandemic influenza are needed.
Keywords: 1918 influenza; cynomolgus macaques; influenza model; rhesus macaque.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Herfst S, Schrauwen EJA, Linster M, Chutinimitkul S, de Wit E, Munster VJ, Sorrell EM, Bestebroer TM, Burke DF, Smith DJ, Rimmelzwaan GF, Osterhaus ADME, Fouchier RAM. 2012. Airborne transmission of influenza A/H5N1 virus between ferrets. Science 336:1534–1541. 10.1126/science.1213362. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Imai M, Watanabe T, Hatta M, Das SC, Ozawa M, Shinya K, Zhong G, Hanson A, Katsura H, Watanabe S, Li C, Kawakami E, Yamada S, Kiso M, Suzuki Y, Maher EA, Neumann G, Kawaoka Y. 2012. Experimental adaptation of an influenza H5 HA confers respiratory droplet transmission to a reassortant H5 HA/H1N1 virus in ferrets. Nature 486:420–428. 10.1038/nature10831. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Wit E, Siegers JY, Cronin JM, Weatherman S, Van Den Brand JM, Leijten LM, Van Run P, Begeman L, Van Den Ham HJ, Andeweg AC, Bushmaker T, Scott DP, Saturday G, Munster VJ, Feldmann H, Van Riel D. 2018. 1918 H1N1 influenza virus replicates and induces proinflammatory cytokine responses in extrarespiratory tissues of ferrets. J Infect Dis 217:1237–1246. 10.1093/infdis/jiy003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

