The frequency of efflux pump genes expression in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from pulmonary secretions
- PMID: 35925415
- PMCID: PMC9352836
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-022-01444-4
The frequency of efflux pump genes expression in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from pulmonary secretions
Abstract
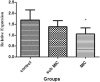
Acinetobacter baumannii is an important opportunistic pathogen, and the cause of nosocomial infections worldwide in recent decades. Efflux pumps are considered as the important causes of multidrug resistance of A. baumannii. The aim of this study was to determine the frequency of efflux pump genes, and evaluate the antibiotic effect of Tigecycline on the expression of adeB gene in isolates of multidrug-resistant. A. baumannii. 70 isolates of A. baumannii were collected and confirmed by biochemical and molecular tests. Antibiotic resistance (Ciprofloxacin, Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and Tigecycline) was performed based on the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) method. Then, the effect of Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone inhibitor (CCCP) on isolates was investigated and the frequency of adeB, adeG, adeJ and abeM genes were examined by PCR for isolates with reduced in MIC titer. Also, the antibiotic effect of Tigecycline on adeB gene expression in A. baumannii isolates was analyzed by Real-Time PCR. The antibiotic resistance for Ciprofloxacin, Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and Tigecycline was 97.1%, 95.8% and 37.2%, respectively. Following CCCP inhibitor use, the MIC titer had a decrease in MIC titer containing CCCP inhibitor was 64.3% for Ciprofloxacin, 51.5% for Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and 50% for Tigecycline. The frequencies of genes associated with adeB, adeG, adeJ and abeM efflux pump were 100%, 92.8%, 86% and 98.5%, respectively. Real-Time PCR results showed a correlation between the antibiotic effects of Tigecycline on adeB gene expression. The antibiotic resistance of the isolates was relatively high. The isolates were resistant to Ciprofloxacin and Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole antibiotics, while more sensitive to Tigecycline. Also, efflux pump genes, which are the antibiotic resistance factors of A. baumannii, are frequently high in the isolates but it seems that isolates use other effluxe pumps than RND family to exit tigecycline.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; Baumannii; Efflux Pump; Tigecycline.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Afshar Yavari S, Rota S, Caglar K, Fidan I. Determination of resistance pattern of isolated Acintobacter baumannii from intensive care units (ICUS) in Gazi Hospital, Ankara. Nurs Midwifery J. 2016;13(10):912–928.
-
- Aladel R, Abdalsameea S, Badwy H, Refat S, ElKholy R. Role of AdeB gene in multidrug-resistance Acinetobacter. Menoufia Med J Medknow. 2020;33(1):205. doi: 10.4103/mmj.mmj_434_18. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources