Child Deaths by Gun Violence in the US During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 35925607
- PMCID: PMC9353595
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.25339
Child Deaths by Gun Violence in the US During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
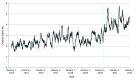
This cross-sectional study examines gun-related deaths during the early stages of the US COVID-19 pandemic among children aged 0 to 17 years.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- GVA . Gun Violence Archive. Accessed April 28, 2022. https://www.gunviolencearchive.org/
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

