N-glycolylated carbohydrates in nature
- PMID: 35925816
- PMCID: PMC9764442
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwac048
N-glycolylated carbohydrates in nature
Abstract
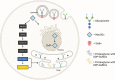
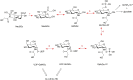
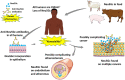
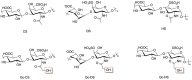
N-glycolylated carbohydrates are amino sugars with an N-glycolyl amide group. These glycans have not been well studied due to their surprising rarity in nature in comparison with N-acetylated carbohydrates. Recently, however, there has been increasing interest in N-glycolylated sugars because the non-human sialic acid N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc), apparently the only source of all N-glycolylated sugars in deuterostomes, appears to be involved in xenosialitis (inflammation associated with consumption of Neu5Gc-rich red meats). Xenosialitis has been implicated in cancers as well as other diseases including atherosclerosis. Furthermore, metabolites of Neu5Gc have been shown to be incorporated into glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), resulting in N-glycolylated GAGs. These N-glycolylated GAGs have important potential applications, such as dating the loss of the Neu5Gc-generating CMAH gene in humans and being explored as a xenosialitis biomarker and/or estimate of the body burden of diet-derived Neu5Gc, to understand the risks associated with the consumption of red meats. This review explores N-glycolylated carbohydrates, how they are metabolized to N-glycolylglucosamine and N-glycolylgalactosamine, and how these metabolites can be incorporated into N-glycolylated GAGs in human tissues. We also discuss other sources of N-glycolylated sugars, such as recombinant production from microorganisms using metabolic engineering as well as chemical synthesis.
Keywords: N-glycolyl; chondroitin; glycobiology; neuraminic acid; xenosialitis.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Alviano CS, Pereira MEA, Souza W, Oda LM, Travassos LR. Sialic acids are surface components of Sporothrix Schenckii yeast forms. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1982:15(3):223–228.
-
- Awofiranye AE, Hudson J, Tithi AD, Linhardt RJ, Vongsangnak W, Koffas MAG. Chondroitin sulfate and its derivatives: A review of microbial and other production methods. Fermentation. 2022:8(7):323.

