A circuit mechanism for independent modulation of excitatory and inhibitory firing rates after sensory deprivation
- PMID: 35925891
- PMCID: PMC9371725
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2116895119
A circuit mechanism for independent modulation of excitatory and inhibitory firing rates after sensory deprivation
Abstract
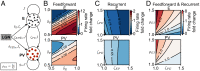
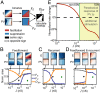
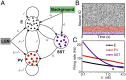
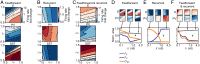
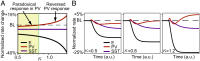
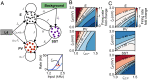
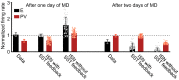
Diverse interneuron subtypes shape sensory processing in mature cortical circuits. During development, sensory deprivation evokes powerful synaptic plasticity that alters circuitry, but how different inhibitory subtypes modulate circuit dynamics in response to this plasticity remains unclear. We investigate how deprivation-induced synaptic changes affect excitatory and inhibitory firing rates in a microcircuit model of the sensory cortex with multiple interneuron subtypes. We find that with a single interneuron subtype (parvalbumin-expressing [PV]), excitatory and inhibitory firing rates can only be comodulated-increased or decreased together. To explain the experimentally observed independent modulation, whereby one firing rate increases and the other decreases, requires strong feedback from a second interneuron subtype (somatostatin-expressing [SST]). Our model applies to the visual and somatosensory cortex, suggesting a general mechanism across sensory cortices. Therefore, we provide a mechanistic explanation for the differential role of interneuron subtypes in regulating firing rates, contributing to the already diverse roles they serve in the cortex.
Keywords: cortical circuits; interneurons; network model; sensory deprivation; synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Letzkus J. J., et al. ., A disinhibitory microcircuit for associative fear learning in the auditory cortex. Nature 480, 331–335 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

