Associations between cognitive function and endogenous levels of estradiol and testosterone in adults with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 35926332
- PMCID: PMC10162709
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108268
Associations between cognitive function and endogenous levels of estradiol and testosterone in adults with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Aims: To assess associations that endogenous estradiol and testosterone levels have with cognitive function in older adults with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: We use data from the Look AHEAD clinical trial of behavioral weight loss. Endogenous estradiol and total testosterone levels were determined using stored serum from 996 individuals, mean age 69 years, at two times (averaging 4 years apart) during years 8-18 of follow-up. One to four standardized assessments of attention, executive function, memory, and verbal fluency were collected during this follow-up. Mixed effects models and multiple imputation were used to assess associations that estradiol and total testosterone levels had with body mass index and cognitive function.
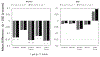
Results: Estradiol levels were not associated with cognitive function in either sex. Total testosterone levels were not associated with cognitive function in women, but greater total testosterone levels were associated with better verbal fluency in men (p < 0.001), most strongly among those carrying the APOE-e4 allele (interaction p = 0.02). The weight loss intervention left a legacy of relatively lower cognitive functioning among women, which was not mediated by current levels of sex hormones.
Conclusions: Behavioral weight loss intervention does not affect cognitive functioning through mechanisms related to estradiol or testosterone.
Clinicaltrials: gov Identifier: NCT00017953.
Keywords: Obesity; Sex differences; Sex hormones; Weight loss.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors have no actual or potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endogenous estradiol and testosterone levels are associated with cognitive performance in older women and men.Horm Behav. 2002 May;41(3):259-66. doi: 10.1006/hbeh.2002.1770. Horm Behav. 2002. PMID: 11971659
-
Low testosterone levels relate to poorer cognitive function in women in an APOE-ε4-dependant manner.Biol Sex Differ. 2024 Jun 5;15(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00620-4. Biol Sex Differ. 2024. PMID: 38835072 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous sex hormones and cognitive function in older men.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999 Oct;84(10):3681-5. doi: 10.1210/jcem.84.10.6086. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. PMID: 10523014
-
Effect of a Long-Term Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on Cognitive Function: Action for Health in Diabetes Study.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017 May;65(5):966-972. doi: 10.1111/jgs.14692. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017. PMID: 28067945 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term Change in Physiological Markers and Cognitive Performance in Type 2 Diabetes: The Look AHEAD Study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Dec 1;105(12):e4778-91. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa591. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32845968 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 DK057151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092237/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058571/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG045334/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG073697/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

