Prenatal environmental stressors impair postnatal microglia function and adult behavior in males
- PMID: 35926455
- PMCID: PMC9438555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111161
Prenatal environmental stressors impair postnatal microglia function and adult behavior in males
Abstract
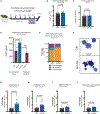
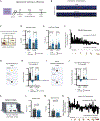
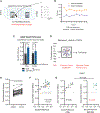
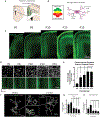
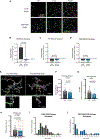
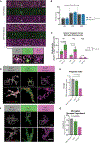
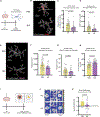
Gestational exposure to environmental toxins and socioeconomic stressors is epidemiologically linked to neurodevelopmental disorders with strong male bias, such as autism. We model these prenatal risk factors in mice by co-exposing pregnant dams to an environmental pollutant and limited-resource stress, which robustly activates the maternal immune system. Only male offspring display long-lasting behavioral abnormalities and alterations in the activity of brain networks encoding social interactions. Cellularly, prenatal stressors diminish microglial function within the anterior cingulate cortex, a central node of the social coding network, in males during early postnatal development. Precise inhibition of microglial phagocytosis within the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) of wild-type (WT) mice during the same critical period mimics the impact of prenatal stressors on a male-specific behavior, indicating that environmental stressors alter neural circuit formation in males via impairing microglia function during development.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; air pollution; maternal immune activation; microglia; neurodevelopmental disorders; prenatal stressors; synapse.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Apprill A, McNally S, Parsons R, and Weber L (2015). Minor revision to V4 region SSU rRNA 806R gene primer greatly increases detection of SAR11 bacterioplankton. Aquat. Microb. Ecol 75, 129–137.
-
- Barnett L, and Seth AK (2014). The MVGC multivariate Granger causality toolbox: a new approach to Granger-causal inference. J. Neurosci. Methods 223, 50–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

