Association of country economy and socioeconomic factors on risk factor control for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes mellitus: Insights from the DISCOVER study
- PMID: 35926587
- PMCID: PMC9647648
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2022.07.008
Association of country economy and socioeconomic factors on risk factor control for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes mellitus: Insights from the DISCOVER study
Abstract
Background: We sought to describe global patterns in achievement of risk factor control for primary prevention in patients with T2D and explore the association of country's GNI/capita with risk factor control.
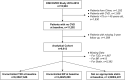
Methods: The DISCOVER study is a prospective, observational study of patients with T2D from 38 countries enrolled at initiation of second-line glucose-lowering therapy. We examined achievement of risk factor control (glycosylated hemoglobin <7%, blood pressure <140/90 mmHg, prescription of a statin) at 3 years among those without optimal control at baseline. Countries were stratified by gross national income (GNI)/capita, from 2017). We examined the impact of country GNI/capita with achievement of risk factor control.
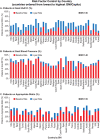
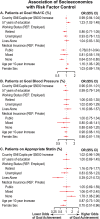
Findings: Our cohort included 9613 patients with T2D and without baseline cardiovascular disease (mean age 57.2 ± 8.7 years, 47.9% women). At baseline, 6354/7646 patients (83.1%) had suboptimal glucose control, 3449/9200 patients (37.5%) had suboptimal BP control, and 2800/4221 patients (66.7%) were not on an appropriate statin (sample sizes differed due to missing covariate data). Optimal control at 3 years of follow-up was achieved in 41% (glucose), 56% (blood pressure), and 29% (statins) of patients. There was significant variability in achievement of risk factor control across countries but no association between country GNI/capita with achievement of risk factor control (p > 0.08 for all).
Interpretation: In a global, prospective study of patients with T2D, we found that cardiovascular risk factor control achievement was suboptimal despite 3 years of follow-up in specialized health care systems. Neither country-level nor patient-level socioeconomic factors fully explained this finding.
Keywords: Primary prevention; Risk factor control; Type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Cardiological Society of India. Published by Elsevier, a division of RELX India, Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Cho N.H., Shaw J.E., Karuranga S., et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;138:271–281. - PubMed
-
- Unnikrishnan R., Pradeepa R., Joshi S.R., Mohan V. Type 2 diabetes: demystifying the global epidemic. Diabetes. 2017;66(6):1432–1442. - PubMed
-
- Tancredi M., Rosengren A., Svensson A.M., et al. Excess mortality among persons with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(18):1720–1732. - PubMed
-
- Ali M.K., Bullard K.M., Saaddine J.B., Cowie C.C., Imperatore G., Gregg E.W. Achievement of goals in U.S. diabetes care, 1999-2010. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(17):1613–1624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

