Efficacy, safety and immunogenicity of hexavalent rotavirus vaccine in Chinese infants
- PMID: 35926726
- PMCID: PMC9583109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.07.011
Efficacy, safety and immunogenicity of hexavalent rotavirus vaccine in Chinese infants
Abstract
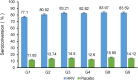
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter trial was conducted in healthy Chinese infants to assess the efficacy and safety of a hexavalent live human-bovine reassortant rotavirus vaccine (HRV) against rotavirus gastroenteritis (RVGE). A total of 6400 participants aged 6-12 weeks were enrolled and randomly assigned to either HRV (n = 3200) or placebo (n = 3200) group. All the subjects received three oral doses of vaccine four weeks apart. The vaccine efficacy (VE) against RVGE caused by rotavirus serotypes contained in HRV was evaluated from 14 days after three doses of administration up until the end of the second rotavirus season. VE against severe RVGE, VE against RVGE hospitalization caused by serotypes contained in HRV, and VE against RVGE, severe RVGE, and RVGE hospitalization caused by natural infection of any serotype of rotavirus were also investigated. All adverse events (AEs) were collected for 30 days after each dose. Serious AEs (SAEs) and intussusception cases were collected during the entire study. Our data showed that VE against RVGE caused by serotypes contained in HRV was 69.21% (95%CI: 53.31-79.69). VE against severe RVGE and RVGE hospitalization caused by serotypes contained in HRV were 91.36% (95%CI: 78.45-96.53) and 89.21% (95%CI: 64.51-96.72) respectively. VE against RVGE, severe RVGE, and RVGE hospitalization caused by natural infection of any serotype of rotavirus were 62.88% (95%CI: 49.11-72.92), 85.51% (95%CI: 72.74-92.30) and 83.68% (95%CI: 61.34-93.11). Incidences of AEs from the first dose to one month post the third dose in HRV and placebo groups were comparable. There was no significant difference in incidences of SAEs in HRV and placebo groups. This study shows that this hexavalent reassortant rotavirus vaccine is an effective, well-tolerated, and safe vaccine for Chinese infants.
Keywords: Efficacy; Infants; Rotavirus gastroenteritis (RVGE); Safety; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of a pentavalent live human-bovine reassortant rotavirus vaccine (RV5) in healthy Chinese infants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Vaccine. 2017 Oct 13;35(43):5897-5904. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.08.081. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Vaccine. 2017. PMID: 28935470 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy, immunogenicity and safety of a trivalent live human-lamb reassortant rotavirus vaccine (LLR3) in healthy Chinese infants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Vaccine. 2020 Oct 27;38(46):7393-7400. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.04.038. Epub 2020 May 23. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 32451212 Clinical Trial.
-
Analyses of health outcomes from the 5 sites participating in the Africa and Asia clinical efficacy trials of the oral pentavalent rotavirus vaccine.Vaccine. 2012 Apr 27;30 Suppl 1:A24-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.08.124. Vaccine. 2012. PMID: 22520132 Clinical Trial.
-
Rotavirus live, oral, pentavalent vaccine.Clin Ther. 2007 Dec;29(12):2724-37. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.12.018. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18201590 Review.
-
Association of Rotavirus Vaccines With Reduction in Rotavirus Gastroenteritis in Children Younger Than 5 Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials and Observational Studies.JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Jul 1;175(7):e210347. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.0347. Epub 2021 Jul 6. JAMA Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33970192 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genotype analysis of rotaviruses isolated from children during a phase III clinical trial with the hexavalent rotavirus vaccine in China.Virol Sin. 2023 Dec;38(6):889-899. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.11.002. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Virol Sin. 2023. PMID: 37972894 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into recent advancements in human and animal rotavirus vaccines: Exploring new frontiers.Virol Sin. 2025 Feb;40(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2024.12.001. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Virol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39672271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and Immunogenicity of a New Rotavirus-Inactivated Vaccine in the Chinese Adolescent Population: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase I Clinical Trial.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Mar 30;13(4):369. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13040369. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40333214 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of vaccination with different types of rotavirus vaccines on the incidence of intussusception: a randomized controlled meta-analysis.Front Pediatr. 2023 Jul 31;11:1239423. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1239423. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37583623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of interventions to improve vaccine efficacy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2025 May 9;14(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13643-025-02856-6. Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40346627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan I.S.F., Bohidar N.R. Exact power and sample size for vaccine efficacy studies. Commu. Stat-Theory Methods. 1998;27:1305–1322.
-
- Chen D., Liu C., Lv H., Shi H., Shang J., Yin Y., Luo P., Luo W. Investigation on rotavirus diarrhea in infants aged two years and below in Yuhan. Prev. Med. 2019;31:628–630. (In Chinese)
-
- Chen H., Li Q., Duan K., Shi C., Zhang D., Dong B., Bai X., Qiao J., Xu G., Yang X., Gao Z., Li F., Lv H., Zhou H., Yan T., Shi H. Molecular epidemiological characteristics of rotavirus VP7 gene in zhengding county of Hebei province, xiangtan county of hunan province and yuhuan city of Zhejiang province, China from 2016 to 2017. Chin J Biologicals. 2021;34:415–427. (In Chinese)
-
- Ciarlet M., Schodel F. Development of a rotavirus vaccine: clinical safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the pentavalent rotavirus vaccine. RotaTeq. Vaccine. 2009;27(Suppl. 6):G72–G81. - PubMed
-
- Clements-Mann M.L., Dudas R., Hoshino Y., Nehring P., Sperber E., Wagner M., Stephens I., Karron R., Deforest A., Kapikian A.Z. Safety and immunogenicity of live attenuated quadrivalent human-bovine (UK) reassortant rotavirus vaccine administered with childhood vaccines to infants. Vaccine. 2001;19:4676–4684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical