Serum stratifin and presepsin as candidate biomarkers for early detection of COVID-19 disease progression
- PMID: 35926945
- PMCID: PMC9188980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jphs.2022.06.002
Serum stratifin and presepsin as candidate biomarkers for early detection of COVID-19 disease progression
Abstract
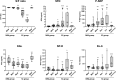
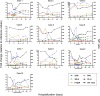
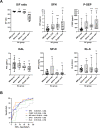
The prognosis of patients with severe cases of COVID-19 is poor; thus, biomarkers for earlier prediction of COVID-19 progression are vital. We measured levels of five lung injury-related biomarkers, SP-D, KL-6, presepsin, kallistatin and stratifin, in serum samples collected serially during hospitalization from 31 patients with mild/moderate or severe/critical COVID-19 pneumonia, and their predictive performances were compared. Like the previously reported presepsin, a new biomarker candidate, stratifin, was significantly elevated with the onset of severe or critical symptoms in COVID-19 patients and decreased with symptom improvement. Notably, changes in stratifin and presepsin levels were distinctly earlier than those in SP-D, KL-6 and even SpO2/FiO2 values. Furthermore, serum levels of these biomarkers were significantly higher at the pre-severe stage (before the start of oxygen support) of patients who eventually advanced to severe/critical stages than in the patients who remained at the mild/moderate stage. These results were confirmed in an independent cohort, including 71 mild/moderate and 14 severe/critical patients, for whom the performance of stratifin and presepsin in discriminating between mild/moderate and pre-severe conditions of COVID-19 patients was superior to that of the SpO2/FiO2 ratio. Therefore, we concluded that stratifin and presepsin could be used as prognostic biomarkers for severe COVID-19 progression.
Keywords: COVID-19; Predictive biomarker; Presepsin; Stratifin.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Ishikawa N., Hattori N., Yokoyama A., Kohno N. Utility of KL-6/MUC1 in the clinical management of interstitial lung diseases. Respir Investig. 2012;50(1):3–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

