The molecular mechanism of snake short-chain α-neurotoxin binding to muscle-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
- PMID: 35927270
- PMCID: PMC9352773
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32174-7
The molecular mechanism of snake short-chain α-neurotoxin binding to muscle-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: The molecular mechanism of snake short-chain α-neurotoxin binding to muscle-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.Nat Commun. 2024 May 28;15(1):4532. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48904-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38806512 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
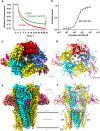
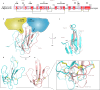
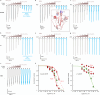
Bites by elapid snakes (e.g. cobras) can result in life-threatening paralysis caused by venom neurotoxins blocking neuromuscular nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Here, we determine the cryo-EM structure of the muscle-type Torpedo receptor in complex with ScNtx, a recombinant short-chain α-neurotoxin. ScNtx is pinched between loop C on the principal subunit and a unique hairpin in loop F on the complementary subunit, thereby blocking access to the neurotransmitter binding site. ScNtx adopts a binding mode that is tilted toward the complementary subunit, forming a wider network of interactions than those seen in the long-chain α-Bungarotoxin complex. Certain mutations in ScNtx at the toxin-receptor interface eliminate inhibition of neuronal α7 nAChRs, but not of human muscle-type receptors. These observations explain why ScNtx binds more tightly to muscle-type receptors than neuronal receptors. Together, these data offer a framework for understanding subtype-specific actions of short-chain α-neurotoxins and inspire strategies for design of new snake antivenoms.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Nirthanan, S., Awal, W. & Niranjan, N. R. Snake α-Neurotoxins and the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. 10.1007/978-94-007-6648-8 (2016).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

