Age-dependent cognitive impairment, hydrocephalus and leukocyte infiltration in transgenic mice with endothelial expression of human EPHX2
- PMID: 35927273
- PMCID: PMC9256583
- DOI: 10.1038/s41514-022-00090-1
Age-dependent cognitive impairment, hydrocephalus and leukocyte infiltration in transgenic mice with endothelial expression of human EPHX2
Abstract
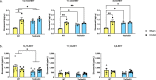
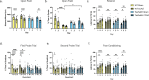
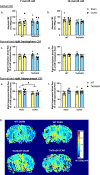
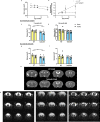
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is upregulated in microvascular endothelium of human brain with vascular cognitive impairment (VCI). Transgenic endothelial expression of human sEH in mice (Tie2hsEH) induces endothelial dysfunction (ED), a pathogenetic mechanism of VCI. We sought to determine if endothelial upregulation of sEH is sufficient to cause cognitive impairment, and if cognitive impairment due to chronic hypoperfusion induced by unilateral common carotid artery occlusion (CCAO) is exacerbated in Tie2hsEH mice. Behavioral performance was assessed by the open field, rotarod, novel object, Morris water maze and fear conditioning tests. Cerebral blood flow and brain morphology were evaluated by MRI, and inflammatory changes investigated using immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry. We demonstrate that transgenic endothelial expression of sEH is sufficient to induce cognitive impairment, associated with leukocyte infiltration, brain atrophy and accelerated, age-dependent ventriculomegaly, identifying ED and sEH upregulation as potential underlying mechanisms and therapeutic targets for VCI.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Financial competing interests are as follows: N.J.A. is co-inventor of technologies related to sEH and EETs signaling that have been licensed by OHSU and JHU to Precision Molecular and Vasocardea. This potential conflict of interest has been reviewed and managed by OHSU. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

