Improving MGMT methylation status prediction of glioblastoma through optimizing radiomics features using genetic algorithm-based machine learning approach
- PMID: 35927323
- PMCID: PMC9352871
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-17707-w
Improving MGMT methylation status prediction of glioblastoma through optimizing radiomics features using genetic algorithm-based machine learning approach
Abstract
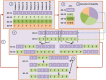
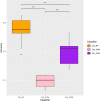
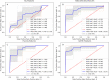
O6-Methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation was shown in many studies to be an important predictive biomarker for temozolomide (TMZ) resistance and poor progression-free survival in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) patients. However, identifying the MGMT methylation status using molecular techniques remains challenging due to technical limitations, such as the inability to obtain tumor specimens, high prices for detection, and the high complexity of intralesional heterogeneity. To overcome these difficulties, we aimed to test the feasibility of using a novel radiomics-based machine learning (ML) model to preoperatively and noninvasively predict the MGMT methylation status. In this study, radiomics features extracted from multimodal images of GBM patients with annotated MGMT methylation status were downloaded from The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA) public database for retrospective analysis. The radiomics features extracted from multimodal images from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) had undergone a two-stage feature selection method, including an eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) feature selection model followed by a genetic algorithm (GA)-based wrapper model for extracting the most meaningful radiomics features for predictive purposes. The cross-validation results suggested that the GA-based wrapper model achieved the high performance with a sensitivity of 0.894, specificity of 0.966, and accuracy of 0.925 for predicting the MGMT methylation status in GBM. Application of the extracted GBM radiomics features on a low-grade glioma (LGG) dataset also achieved a sensitivity 0.780, specificity 0.620, and accuracy 0.750, indicating the potential of the selected radiomics features to be applied more widely on both low- and high-grade gliomas. The performance indicated that our model may potentially confer significant improvements in prognosis and treatment responses in GBM patients.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fusion Radiomics Features from Conventional MRI Predict MGMT Promoter Methylation Status in Lower Grade Gliomas.Eur J Radiol. 2019 Dec;121:108714. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.108714. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Eur J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31704598
-
Multiregional radiomics features from multiparametric MRI for prediction of MGMT methylation status in glioblastoma multiforme: A multicentre study.Eur Radiol. 2018 Sep;28(9):3640-3650. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5302-1. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29564594
-
Radiomics signature: A potential biomarker for the prediction of MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018 May;47(5):1380-1387. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25860. Epub 2017 Sep 19. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018. PMID: 28926163
-
Quality assessment of the MRI-radiomics studies for MGMT promoter methylation prediction in glioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2024 Sep;34(9):5802-5815. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10594-x. Epub 2024 Feb 3. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38308012 Free PMC article.
-
Clinically Relevant Imaging Features for MGMT Promoter Methylation in Multiple Glioblastoma Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018 Aug;39(8):1439-1445. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5711. Epub 2018 Jul 12. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018. PMID: 30002055 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Research hotspots and development trends in molecular imaging of glioma (2014-2024): A bibliometric review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 20;104(25):e42862. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042862. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40550035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of MGMT methylation status in glioblastoma patients based on radiomics feature extracted from intratumoral and peritumoral MRI imaging.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 29;15(1):27533. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08608-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40730593 Free PMC article.
-
-New frontiers in domain-inspired radiomics and radiogenomics: increasing role of molecular diagnostics in CNS tumor classification and grading following WHO CNS-5 updates.Cancer Imaging. 2024 Oct 7;24(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00769-6. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39375809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptive fine-tuning based transfer learning for the identification of MGMT promoter methylation status.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024 Jul 30;10(5):055018. doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ad6573. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024. PMID: 39029475 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics and AI-Based Prediction of MGMT Methylation Status in Glioblastoma Using Multiparametric MRI: A Hybrid Feature Weighting Approach.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 21;15(10):1292. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15101292. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marijnen CA, van den Berg SM, van Duinen SG, Voormolen JH, Noordijk EM. Radiotherapy is effective in patients with glioblastoma multiforme with a limited prognosis and in patients above 70 years of age: A retrospective single institution analysis. Radiother. Oncol. 2005;75:210–216. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2005.03.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

