Isolation and characterization of phage display-derived scFv antibodies against human parechovirus 1 VP0 protein
- PMID: 35927325
- PMCID: PMC9352675
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-17678-y
Isolation and characterization of phage display-derived scFv antibodies against human parechovirus 1 VP0 protein
Abstract
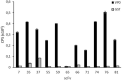
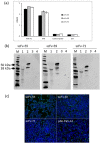
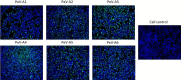
Human parechoviruses (PeVs) are common viruses that are associated with a variety of diseases from mild gastrointestinal and respiratory symptoms to severe central nervous system infections. Until now there has not been antibodies for visualizing parechovirus infection. We used E. coli recombinant PeV-A1-VP0 protein as a target in phage display single chain variable fragment (scFv) antibody library panning. Three rounds of panning allowed identification and isolation of several candidate scFv clones, which tested positive in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) against VP0. Three scFv clones (scFv-55, -59 and -71) with different CDR-3 sequences were further purified and tested in ELISA, Western blot and immunofluorescence microscopy (IFA) against a set of PeV-A1 isolates and a few isolates representing PeV types 2-6. In IFA, all three scFv binders recognized twenty PeV-A1 isolates. ScFv-55 and -71 also recognized clinical representatives of PeV types 1-6 both in IFA and in capture ELISA, while scFv-59 only recognized PeV-A1, -A2 and -A6. PeV-A1-VP0 (Harris strain) sequence was used to generate a peptide library, which allowed identification of a putative unique conformational antibody epitope with fully conserved flanking regions and a more variable core VVTYDSKL, shared between the scFv antibodies. Sequencing of the VP0 region of virus samples and sequence comparisons against parechoviral sequences in GenBank revealed 107 PeV-A1, -A3, -A8, -A17, -A (untyped) sequences with this exact epitope core sequence, which was most dominant among PeV-A1 isolates. These data suggest the first-time isolation of broad range phage display antibodies against human parechoviruses that may be used in diagnostic antibody development.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. ScFv antibodies described in this article are a property of University of Turku, Turku, Finland.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monoclonal antibody against VP0 recognizes a broad range of human parechoviruses.J Virol Methods. 2021 Jul;293:114167. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114167. Epub 2021 Apr 21. J Virol Methods. 2021. PMID: 33894205
-
Detection of Parechovirus A1 with Monoclonal Antibody against Capsid Protein VP0.Microorganisms. 2020 Nov 16;8(11):1794. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111794. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33207765 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of human anti-CD20 single-chain variable fragment (scFv) from a Naive human scFv library.Med Oncol. 2022 Aug 23;39(11):177. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01757-1. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35999405 Free PMC article.
-
Production and immunological characterization of the novel single-chain variable fragment (scFv) antibodies against the epitopes on Opisthorchis viverrini cathepsin F (OvCatF).Acta Trop. 2024 Jun;254:107199. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2024.107199. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Acta Trop. 2024. PMID: 38552996
-
Parechovirus A Circulation and Testing Capacities in Europe, 2015-2021.Emerg Infect Dis. 2024 Feb;30(2):234-244. doi: 10.3201/eid3002.230647. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38270192 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-Stranded Variable Fragment Gene Libraries Built for Phage Display: An Updated Review of Design, Selection and Application.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 24;35:e2407049. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2407.07049. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39631781 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benschop K, Thomas X, Serpenti C, Molenkamp R, Wolthers K. High prevalence of human parechovirus (HPeV) genotypes in the Amsterdam region and identification of specific HPeV variants by direct genotyping of stool samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008;46:3965–3970. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01379-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

