Length of biliopancreatic limb in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and its impact on post-operative outcomes in metabolic and obesity surgery-systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35927470
- PMCID: PMC9584808
- DOI: 10.1038/s41366-022-01186-0
Length of biliopancreatic limb in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and its impact on post-operative outcomes in metabolic and obesity surgery-systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is a gold-standard procedure for treatment of obesity and associated comorbidities. No consensus on the optimal design of this operation has been achieved, with various lengths of bypassed small bowel limb lengths being used by bariatric surgeons. This aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to determine whether biliopancreatic limb (BPL) length in RYGB affects postoperative outcomes including superior reduction in weight, body mass index (BMI), and resolution of metabolic comorbidities associated with obesity.
Methods: A systematic search of the literature was conducted up until 1st June 2021. Meta-analysis of primary outcomes was performed utilising a random-effects model. Statistical significance was determined by p value < 0.05.
Results: Ten randomised controlled trials were included in the final quantitative analysis. No difference in outcomes following short versus long BLP in RYGB was identified at 12-72 months post-operatively, namely in BMI reduction, remission or improvement of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidaemia, and complications (p > 0.05). Even though results of four studies showed superior total body weight loss in the long BPL cohorts at 24 months post-operatively (pooled mean difference -6.92, 95% CI -12.37, -1.48, p = 0.01), this outcome was not observed at any other timepoint.
Conclusion: Based on the outcomes of the present study, there is no definitive evidence to suggest that alteration of the BPL affects the quantity of weight loss or resolution of co-existent metabolic comorbidities associated with obesity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
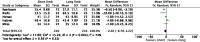
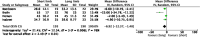
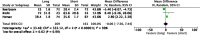
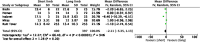
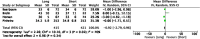
References
-
- Ikramuddin S, Korner J, Lee WJ, Thomas AJ, Connett JE, Bantle JP, et al. Lifestyle intervention and medical management with vs without Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and control of hemoglobin A1c, LDL cholesterol, and systolic blood pressure at 5 years in the diabetes surgery study. JAMA. 2018;319:266–78. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.20813. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simonson DC, Halperin F, Foster K, Vernon A, Goldfine AB. Clinical and patient-centered outcomes in obese patients with type 2 diabetes 3 years after randomization to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery versus intensive lifestyle management: the SLIMM-T2D study. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:670–9. doi: 10.2337/dc17-0487. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

