Differences in brain activity between normal and diabetic rats under isoflurane anesthesia: a resting-state functional MRI study
- PMID: 35927630
- PMCID: PMC9354416
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-022-00867-6
Differences in brain activity between normal and diabetic rats under isoflurane anesthesia: a resting-state functional MRI study
Abstract
Background: Altered neural activity based on the fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (fALFF) has been reported in patients with diabetes. However, whether fALFF can differentiate healthy controls from diabetic animals under anesthesia remains unclear. The study aimed to elucidate the changes in fALFF in a rat model of diabetes under isoflurane anesthesia.
Methods: The first group of rats (n = 5) received a single intraperitoneal injection of 70 mg/kg streptozotocin (STZ) to cause the development of diabetes. The second group of rats (n = 7) received a single intraperitoneal injection of the same volume of solvent. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging was used to assess brain activity at 4 weeks after STZ or solvent administration.
Results: Compared to the healthy control animals, rats with diabetes showed significantly decreased fALFF in various brain regions, including the cingulate cortex, somatosensory cortex, insula, and striatum (all P < 0.05). The decreased fALFF suggests the aberrant neural activities in the diabetic rats. No regions were detected in which the control group had a lower fALFF than that in the diabetes group.
Conclusions: The results of this study demonstrated that the fALFF could be used to differentiate healthy controls from diabetic animals, providing meaningful information regarding the neurological pathophysiology of diabetes in animal models.
Keywords: Anesthesia; Hyperglycemia; Neural; Streptozotocin (STZ); fALFF.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



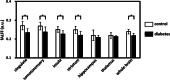
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA, Ogurtsova K, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

