Nintedanib modulates type III collagen turnover in viable precision-cut lung slices from bleomycin-treated rats and patients with pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 35927669
- PMCID: PMC9351157
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-022-02116-4
Nintedanib modulates type III collagen turnover in viable precision-cut lung slices from bleomycin-treated rats and patients with pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Aberrant extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition and remodelling is important in the disease pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis (PF). We characterised neoepitope biomarkers released by ECM turnover in lung tissue from bleomycin-treated rats and patients with PF and analysed the effects of two antifibrotic drugs: nintedanib and pirfenidone.
Methods: Precision-cut lung slices (PCLS) were prepared from bleomycin-treated rats or patients with PF. PCLS were incubated with nintedanib or pirfenidone for 48 h, and levels of neoepitope biomarkers of type I, III and VI collagen formation or degradation (PRO-C1, PRO-C3, PRO-C6 and C3M) as well as fibronectin (FBN-C) were assessed in the culture supernatants.
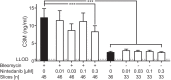
Results: In rat PCLS, incubation with nintedanib led to a reduction in C3M, reflecting type III collagen degradation. In patient PCLS, incubation with nintedanib reduced the levels of PRO-C3 and C3M, thus showing effects on both formation and degradation of type III collagen. Incubation with pirfenidone had a marginal effect on PRO-C3. There were no other notable effects of either nintedanib or pirfenidone on the other neoepitope biomarkers studied.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that nintedanib modulates neoepitope biomarkers of type III collagen turnover and indicated that C3M is a promising translational neoepitope biomarker of PF in terms of therapy assessment.
Keywords: Antifibrotic therapy; Collagen; Extracellular matrix; Human lung; Neoepitope biomarkers; Nintedanib; Pirfenidone; Precision-cut lung slices; Pulmonary fibrosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CH, VB, SK, DJ, KS and AB have nothing to declare. CD and LW are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim, the marketing authorisation holder of nintedanib used in this study. JMBS, SRR, MAK and DJL are full-time employees and stock owners at Nordic Bioscience. JMBS holds patent PRO-C6 assay (US20190309055A1; US20180088129A1). MAK is a patent- holder for assays for C1M (ref. 9359633 [US]), C3M (ref. 9359633 [US]) and PRO-C3 (ref. 9726674 [US]). DJL is a patent- holder for assays for this manuscript. Fraunhofer ITEM is a public, non-profit research organization who perform contract research on behalf of the pharmaceutical and biotech industry.
Figures

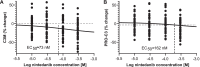
Similar articles
-
Tissue turnover of collagen type I, III and elastin is elevated in the PCLS model of IPF and can be restored back to vehicle levels using a phosphodiesterase inhibitor.Respir Res. 2016 Jul 5;17(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0394-8. Respir Res. 2016. PMID: 27411390 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of Nintedanib and Pirfenidone on lung alveolar epithelial cell function in ex vivo murine and human lung tissue cultures of pulmonary fibrosis.Respir Res. 2018 Sep 15;19(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0876-y. Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 30219058 Free PMC article.
-
Precision-cut lung slices from bleomycin treated animals as a model for testing potential therapies for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Apr;55:75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30776489
-
Efficacy of antifibrotic drugs, nintedanib and pirfenidone, in treatment of progressive pulmonary fibrosis in both idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and non-IPF: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Dec 11;21(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01783-1. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 34895203 Free PMC article.
-
[Antifibrotic therapy and progressive lung fibrosis].Rev Med Suisse. 2020 Jun 17;16(698):1256-1260. Rev Med Suisse. 2020. PMID: 32558455 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Precision cut lung slices: an integrated ex vivo model for studying lung physiology, pharmacology, disease pathogenesis and drug discovery.Respir Res. 2024 Jun 1;25(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02855-6. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38824592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision Cut Lung Slices: Emerging Tools for Preclinical and Translational Lung Research. An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 5;72(1):16-31. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2024-0479ST. Online ahead of print. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39499861 Free PMC article.
-
The Fibrotic Phenotype of Human Precision-Cut Lung Slices Is Maintained after Cryopreservation.Toxics. 2024 Aug 30;12(9):637. doi: 10.3390/toxics12090637. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39330565 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the efficacy of early treatment with pirfenidone on the lung function of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Aug 6;12(22):4913-4923. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.4913. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39109030 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Imaging in Precision-Cut Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Slices.Ann Thorac Surg. 2024 Feb;117(2):458-465. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2023.07.037. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Ann Thorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 37572959 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

