Genistein attenuated oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in L-arginine induced acute pancreatitis in mice
- PMID: 35927726
- PMCID: PMC9351145
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-022-03689-9
Genistein attenuated oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in L-arginine induced acute pancreatitis in mice
Abstract
Aim: Acute pancreatitis is a common and potentially serious condition. However, a specific treatment for this condition is still lacking. Genistein, with its anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, could possibly be used to tackle the underlying pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the effects of genistein on oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in acute pancreatitis induced by L-arginine in mice.
Methods: Twenty-four male ICR mice were equally divided into 4 groups: Control (Con); Acute pancreatitis (AP) group: Two doses of i.p. 350 mg/100 g body weight (BW) of L-arginine were administered 1 h apart; AP and low-dose genistein (LG) group: mice were given i.p. injection of 10 mg/kg genistein 2 h prior to L-arginine injection followed by once-daily dosing for 3 days; and AP and high-dose genistein (HG) group: mice were given 100 mg/kg genistein with the similar protocol as the LG group. Pancreatic tissue was evaluated for histopathological changes and acinar cell apoptosis, malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, immunohistochemical staining for myeloperoxidase (MPO), nuclear factor-kappa beta (NF-kB), and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE). Serum levels of amylase (AMY), c-reactive protein (CRP), and interleukin (IL)-6 were measured.
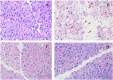
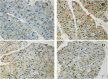
Results: Significant increases in the degree of acinar cell apoptosis, pancreatic MDA, serum IL-6 and amylase, MPO, NF-kB and 4-HNE positivity were observed in the AP group. All these parameters declined after low- and high-dose genistein treatment. Severe pancreatic inflammation, edema, and acinar cell necrosis were observed in the AP group. Significant improvement of histopathological changes was seen in both low- and high-dose genistein groups. There were no significant differences in any parameters between low and high doses of genistein.
Conclusion: Genistein could attenuate the severity of histopathological changes in acute pancreatitis through its anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic properties.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis; Anti-apoptosis; Anti-inflammation; Anti-oxidant; Genistein; Mice.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of curcumin on oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in L-arginine induced acute pancreatitis in mice.Heliyon. 2019 Aug 27;5(8):e02222. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02222. eCollection 2019 Aug. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31485503 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects of resveratrol and β-carotene on L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis through oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways in rats.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):32068. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83764-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738464 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics mixture and taurine attenuate L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis in rats: Impact on transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV-1)/IL-33/NF-κB signaling and apoptosis.Tissue Cell. 2023 Dec;85:102234. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2023.102234. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Tissue Cell. 2023. PMID: 37844391
-
Natural Compounds for the Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis: Novel Anti-Inflammatory Therapies.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 2;14(9):1101. doi: 10.3390/biom14091101. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of plant polyphenols in acute pancreatitis.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Feb;33(2):785-798. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01584-y. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39497005 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of probiotics on pancreatic inflammation and intestinal integrity in mice with acute pancreatitis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 May 22;23(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03998-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37217916 Free PMC article.
-
Electron microscopic analysis of pomegranate and black chokeberry effects on acute pancreatitis in rats.J Mol Histol. 2025 Mar 26;56(2):119. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10380-z. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40133730
-
Identification of Biomarkers Associated with Oxidative Stress and Immune Cells in Acute Pancreatitis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jun 25;17:4077-4091. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S459044. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38948197 Free PMC article.
-
Genistein inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory substances from macrophages by suppressing potassium loss- and ROS-mediated caspase-1/gasdermin D pathway activation and pyroptotic cell lysis.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(12):1506-1514. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.77887.16854. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39539441 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic profiling reveals amino acid dysregulation in congenital heart disease: Arginine-induced embryonic malformations and pathogenic insights.Biomed Rep. 2025 Jul 25;23(4):159. doi: 10.3892/br.2025.2037. eCollection 2025 Oct. Biomed Rep. 2025. PMID: 40777626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frossard JL. Trypsin activation peptide (TAP) in acute pancreatitis: from pathophysiology to clinical usefulness. Jop. 2001;2(2):69–77. - PubMed
-
- Gross V, Leser HG, Heinisch A, Schölmerich J. Inflammatory mediators and cytokines–new aspects of the pathophysiology and assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis? Hepatogastroenterology. 1993;40(6):522–530. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

