Androgen receptor polymorphism, testosterone levels, and prognosis in patients with acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 35928286
- PMCID: PMC9241568
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjopen/oeab023
Androgen receptor polymorphism, testosterone levels, and prognosis in patients with acute myocardial infarction
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to articles in EHJ Open missing data availability statements.Eur Heart J Open. 2024 Jan 16;4(1):oead137. doi: 10.1093/ehjopen/oead137. eCollection 2024 Jan. Eur Heart J Open. 2024. PMID: 38230360 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Aims: Low testosterone has been associated with cardiovascular disease in men but with contradictory findings. Testosterone bind to the androgen receptor and polymorphisms of the receptor gene such as CAG repeat length may affect transcriptional activity, possibly mitigating testosterone effects. The aims were to study the CAG repeat length and testosterone levels at four time points following a myocardial infarction (MI) and to analyse possible relationships between CAG repeat length and cardiovascular prognosis.
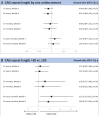
Methods and results: Male patients admitted for acute MI (n = 122) from the Glucose in Acute Myocardial Infarction study were included. Blood samples were drawn at four time points (day after admission, at discharge, and at 3 and 12 months post-infarction) for assessment of testosterone levels. Patients were followed for a median of 11.6 years. Cox regression analyses were performed for CAG repeat length by one unit increment and by > vs. ≤median for cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality. Median CAG repeat length was 20. There was no difference in testosterone levels at each time point when dividing the cohort into ≤ vs. >CAG repeat median (=20). There was no association between CAG repeat length either as a continuous or categorical variable in unadjusted and age-adjusted Cox analyses for cardiovascular events. While CAG >20 was associated with all-cause mortality in unadjusted analyses (hazard ratio 2.19, 95% confidence interval 1.13-4.22; P = 0.02), it did not remain significant following adjustment for age.
Conclusion: CAG repeat length was not associated with testosterone levels or prognosis in men with acute MI.
Keywords: Androgen receptor; Cardiovascular disease; Diabetes; Genetics; Testosterone.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2021. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interactive effects of testosterone and the androgen receptor CAG repeat length polymorphism on cardiovascular-renal events and mortality in men with diabetes.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2019 Jan;35(1):e3081. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3081. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 30261555
-
The androgen receptor CAG repeat polymorphism as a risk factor of low serum testosterone and its cardiometabolic effects in men.Int J Androl. 2012 Aug;35(4):511-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2011.01220.x. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Int J Androl. 2012. PMID: 21950564
-
CAG polymorphic repeat length in androgen receptor gene combined with pretreatment serum testosterone level as prognostic factor in patients with metastatic prostate cancer.Eur Urol. 2005 Apr;47(4):557-63. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2004.10.016. Epub 2004 Dec 16. Eur Urol. 2005. PMID: 15774258
-
Polymorphic Cytosine-Adenine-Guanine Repeat Length of Androgen Receptor Gene and Gender Incongruence in Trans Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies.J Sex Med. 2020 Mar;17(3):543-550. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2019.12.010. Epub 2020 Jan 8. J Sex Med. 2020. PMID: 31926901
-
CAG repeat testing of androgen receptor polymorphism: is this necessary for the best clinical management of hypogonadism?J Sex Med. 2013 Oct;10(10):2373-81. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12268. Epub 2013 Jul 11. J Sex Med. 2013. PMID: 23844628 Review.
Cited by
-
The predictive value of CK-MB on the curative effect of urokinase combined with LMWH calcium in AMI.Biomark Med. 2024 Dec;18(24):1087-1092. doi: 10.1080/17520363.2024.2429367. Epub 2024 Nov 24. Biomark Med. 2024. PMID: 39580633 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Norhammar A, Tenerz A, Nilsson G, Hamsten A, Efendic S, Ryden L, Malmberg K. Glucose metabolism in patients with acute myocardial infarction and no previous diagnosis of diabetes mellitus: a prospective study. Lancet 2002;359:2140–2144. - PubMed
-
- Ritsinger V, Tanoglidi E, Malmberg K, Nasman P, Ryden L, Tenerz A, Norhammar A. Sustained prognostic implications of newly detected glucose abnormalities in patients with acute myocardial infarction: long-term follow-up of the Glucose Tolerance in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction cohort. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2015;12:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Stanworth RD, Kapoor D, Channer KS, Jones TH. Androgen receptor CAG repeat polymorphism is associated with serum testosterone levels, obesity and serum leptin in men with type 2 diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol 2008;159:739–746. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

