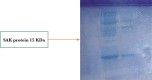
Cloning & expression of SAK enzyme from Staphylococcus aureus in E. coli BL21-CodonPlus
- PMID: 35928367
- PMCID: PMC9321505
- DOI: 10.25122/jml-2021-0335
Cloning & expression of SAK enzyme from Staphylococcus aureus in E. coli BL21-CodonPlus
Abstract
Staphylokinase (SAK), also known as staphylococcal fibrinolysin, is a protein with a molecular mass of about 15 kDa produced by Staphylococcus aureus. Staphylokinase is synthesized in the late exponential phase, similar to streptokinase. The current study identified and predicted the protein SAK from Staphylococcus aureus. SAK is a fibrinolytic enzyme of the third generation that acts as an indirect activator of plasminogen. The current study cloned and expressed SAK protein isolated from Staphylococcus aureus and used in the form of a grid for enhancement of SAK Catalyst with PCR, disengagement, and change into articulation vector PET24b(+). The recombinant plasmid was changed into E. coli strain BL21 (codon additionally to 440) acceptance with isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG).
Keywords: 15 kDa; BL21-CodonPlus; E. coli; IPTG – isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside; Plasmid pET24b(+); SAK – Staphylokinase; Staphylokinase (SAK); r-SAK – recombinant staphylokinase.
©2022 JOURNAL of MEDICINE and LIFE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Green RM, Sambrook J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd ed. 2002. Protocol 8: Purification of Expressed Proteins from Inclusion Bodies; pp. 15–54.
-
- Collen D, Lijnen HR. Staphylokinase, a fibrin-specific plasminogen activator with therapeutic potential? Blood. 1994 Aug 1;84(3):680–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources