Recognition of Glycometabolism-Associated lncRNAs as Prognosis Markers for Bladder Cancer by an Innovative Prediction Model
- PMID: 35928440
- PMCID: PMC9343799
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.918705
Recognition of Glycometabolism-Associated lncRNAs as Prognosis Markers for Bladder Cancer by an Innovative Prediction Model
Abstract
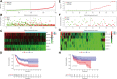
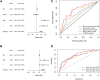
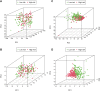
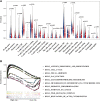
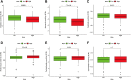
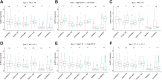
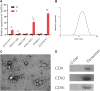
The alteration of glycometabolism is a characteristic of cancer cells. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been documented to occupy a considerable position in glycometabolism regulation. This research aims to construct an effective prediction model for the prognosis of bladder cancer (BC) based on glycometabolism-associated lncRNAs (glyco-lncRNAs). Pearson correlation analysis was applied to get glyco-lncRNAs, and then, univariate cox regression analysis was employed to further filtrate survival time-associated glyco-lncRNAs. Multivariate cox regression analysis was utilized to construct the prediction model to divide bladder cancer (BC) patients into high- and low-risk groups. The overall survival (OS) rates of these two groups were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Next, gene set enrichment analysis and Cibersortx were used to explore the enrichment and the difference in immune cell infiltration, respectively. pRRophetic algorithm was applied to explore the relation between chemotherapy sensitivity and the prediction model. Furthermore, reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction was adopted to detect the lncRNAs constituting the prediction signature in tissues and urine exosomal samples of BC patients. A powerful model including 6 glyco-lncRNAs was proposed, capable of suggesting a risk score for each BC patient to predict prognosis. Patients with high-risk scores demonstrated a shorter survival time both in the training cohort and testing cohort, and the risk score could predict the prognosis without depending on the traditional clinical traits. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of the risk score was higher than that of other clinical traits (0.755 > 0.640, 0.485, 0.644, or 0.568). The high- and low-risk groups demonstrated very distinct immune cells infiltration conditions and gene set enriched terms. Besides, the high-risk group was more sensitive to cisplatin, docetaxel, and sunitinib. The expression of lncRNA AL354919.2 featured with an increase in low-grade patients and a decrease in T3-4 and Stage III-IV patients. Based on the experiment results, lncRNA AL355353.1, AC011468.1, and AL354919.2 were significantly upregulated in tumor tissues. This research furnishes a novel reference for predicting the prognosis of BC patients, assisting clinicians with help in the choice of treatment.
Keywords: bioinformatics; bladder cancer; glycometabolism; lncRNA; prognosis prediction.
Copyright © 2022 Tang, Li, Tang, Zheng, Luo, Li, Li, Wang and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
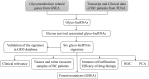

Similar articles
-
A New Ferroptosis-Related lncRNA Signature Predicts the Prognosis of Bladder Cancer Patients.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 16;9:699804. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.699804. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34869304 Free PMC article.
-
A prognostic index based on a fourteen long non-coding RNA signature to predict the recurrence-free survival for muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020 Jul 9;20(Suppl 3):136. doi: 10.1186/s12911-020-1115-2. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020. PMID: 32646427 Free PMC article.
-
A robust signature of immune-related long non-coding RNA to predict the prognosis of bladder cancer.Cancer Med. 2021 Sep;10(18):6534-6545. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4167. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34374227 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network identifies four-lncRNA signature as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer.J Transl Med. 2018 Sep 27;16(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1640-2. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30261893 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of Six Autophagy-related Long Non-coding RNAs as Prognostic Signature in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 1;18(1):88-98. doi: 10.7150/ijms.49449. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33390777 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of platinum resistance-related gene signature for prognosis and immune analysis in bladder cancer.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 26;14:1062060. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1062060. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36777726 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications in Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 11;15(5):1465. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051465. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting DAD1 gene with CRISPR-Cas9 system transmucosally delivered by fluorinated polylysine nanoparticles for bladder cancer intravesical gene therapy.Theranostics. 2024 Jan 1;14(1):203-219. doi: 10.7150/thno.88550. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38164146 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

