Research hotspots and emerging trends of deep learning applications in orthopedics: A bibliometric and visualized study
- PMID: 35928480
- PMCID: PMC9343683
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.949366
Research hotspots and emerging trends of deep learning applications in orthopedics: A bibliometric and visualized study
Abstract
Background: As a research hotspot, deep learning has been continuously combined with various research fields in medicine. Recently, there is a growing amount of deep learning-based researches in orthopedics. This bibliometric analysis aimed to identify the hotspots of deep learning applications in orthopedics in recent years and infer future research trends.
Methods: We screened global publication on deep learning applications in orthopedics by accessing the Web of Science Core Collection. The articles and reviews were collected without language and time restrictions. Citespace was applied to conduct the bibliometric analysis of the publications.
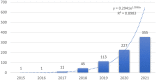
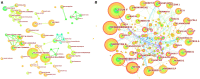
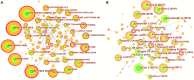
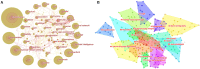
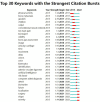
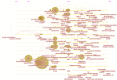
Results: A total of 822 articles and reviews were finally retrieved. The analysis showed that the application of deep learning in orthopedics has great prospects for development based on the annual publications. The most prolific country is the USA, followed by China. University of California San Francisco, and Skeletal Radiology are the most prolific institution and journal, respectively. LeCun Y is the most frequently cited author, and Nature has the highest impact factor in the cited journals. The current hot keywords are convolutional neural network, classification, segmentation, diagnosis, image, fracture, and osteoarthritis. The burst keywords are risk factor, identification, localization, and surgery. The timeline viewer showed two recent research directions for bone tumors and osteoporosis.
Conclusion: Publications on deep learning applications in orthopedics have increased in recent years, with the USA being the most prolific. The current research mainly focused on classifying, diagnosing and risk predicting in osteoarthritis and fractures from medical images. Future research directions may put emphasis on reducing intraoperative risk, predicting the occurrence of postoperative complications, screening for osteoporosis, and identification and classification of bone tumors from conventional imaging.
Keywords: Citespace; bibliometric analysis; deep learning; orthopedics; research trends.
Copyright © 2022 Feng, Zhou, Wang, He, Li and Tu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The top 100 most cited articles on intramedullary nail fixation from 2018-2022: a bibliometric and visualized analysis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024 Mar;28(5):1662-1679. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202403_35582. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38497851 Review.
-
Mapping knowledge landscapes and emerging trends of the links between osteoarthritis and osteoporosis: A bibliometric analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Dec 19;10:1019691. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1019691. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36600941 Free PMC article.
-
Trends and hotspots in research on medical images with deep learning: a bibliometric analysis from 2013 to 2023.Front Artif Intell. 2023 Nov 9;6:1289669. doi: 10.3389/frai.2023.1289669. eCollection 2023. Front Artif Intell. 2023. PMID: 38028662 Free PMC article.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Trends and hotspots in research on osteoporosis and nutrition from 2004 to 2024: a bibliometric analysis.J Health Popul Nutr. 2024 Nov 30;43(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s41043-024-00690-5. J Health Popul Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39616355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Application of Artificial Intelligence in Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review Based on Bibliometric Analysis.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(11):1280-1290. doi: 10.2174/0118715303264254231117113456. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38178659
-
Emergent trends in organ-on-a-chip applications for investigating metastasis within tumor microenvironment: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 9;10(1):e23504. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23504. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38187238 Free PMC article.
-
Re-tear after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair can be predicted using deep learning algorithm.Front Artif Intell. 2024 Feb 29;7:1331853. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1331853. eCollection 2024. Front Artif Intell. 2024. PMID: 38487743 Free PMC article.
-
Post-operative infections after cardiothoracic surgery and vascular procedures: a bibliometric and visual analysis of the 100 most-cited articles in the past 2 decades.GMS Hyg Infect Control. 2024 May 17;19:Doc29. doi: 10.3205/dgkh000484. eCollection 2024. GMS Hyg Infect Control. 2024. PMID: 38883404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global hotspots and emerging trends in 3D bioprinting research.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 May 25;11:1169893. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1169893. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37304138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun ACM. (2017) 60:84–90. 10.1145/3065386 - DOI
-
- Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J. IEEE (editors). Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. 27th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Columbus, OH: (2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

